Dipyridamole dosages: 100 mg, 25 mg
Dipyridamole packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills, 120 pills

Discount dipyridamole 100 mg with visa
This impact has been described as a membrane-stabilizing motion prehypertension la gi order dipyridamole 25 mg visa, a quinidinelike impact blood pressure zero gravity trusted dipyridamole 100 mg, or a neighborhood anesthetic effect. The metabolites are basically inactive as -receptor blocking agents and are eradicated primarily by renal excretion. Peak plasma ranges happen 2 to 4 hours after oral administration; the plasma halflife of timolol is approximately 5. The in depth tissue distribution of timolol into lung, liver, and kidney is just like that of other -blockers. Approximately 70% of the drug is excreted within the urine within 24 hours, largely as highly polar unconjugated metabolites. The drug apparently can attain the systemic circulation after intraocular instillation, however plasma levels are only about 7% of those achieved within the aqueous humor. Approximately 25% of the drug is bound to plasma proteins, and its plasma halflife is about 4 hours. Metabolism of acebutolol produces a metabolite with -blocking activity whose half-life is 10 hours. The drug is eradicated primarily by the kidney and in distinction to propranolol, undergoes little hepatic metabolism. Its plasma half-life is roughly 6 hours, though if it is administered to a patient with impaired renal perform, its half-life could be significantly extended. The drug is topic to a slight first-pass impact such that the absolute bioavailability of the drug is about 90%. The major route of elimination is by liver metabolism, with solely 15% of unchanged drug being excreted. It is almost fully absorbed and reveals about 30% binding to plasma proteins. The -blocker esmolol (Brevibloc) is unusual in that it is rather rapidly metabolized; its plasma half-life is only 9 minutes. It is topic to hydrolysis by cytosolic esterases in purple blood cells to yield methanol and an acid metabolite, the latter having an elimination half-life of about four hours. Because of its rapid onset and short period of action, esmolol is utilized by the intravenous route for the management of ventricular arrhythmias in emergencies. Nadolol (Corgard) is slowly and incompletely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, and only 30% of an orally administered dose is absorbed. The plasma half-life is sort of lengthy, approaching 24 hours, which allows dosing once per day. First-pass metabolism is estimated at about 15%, and its plasma half-life is on the order of 3 to four hours. Pharmacological Actions an important actions of the -blocking drugs are on the cardiovascular system. These results are most pronounced when sympathetic exercise is excessive or when the guts is stimulated by circulating agonists. This is due to the compensatory reflex enhance in peripheral vascular resistance that outcomes from a -blocker�induced decrease in cardiac output. Chronic administration of -blockers, however, results in a discount of blood stress, and this is the reason for their use in primary hypertension (see Chapter 20). This impact may be due partially to the unopposed -receptor�mediated vasoconstriction that follows -receptor blockade in the coronary arteries. Additional contributing components to the lower in coronary blood move are the adverse chronotropic and inotropic effects produced by the -blockers; these actions end in a decrease in the amount of blood available for the coronary system. The lower in mean blood strain may contribute to the lowered coronary blood circulate. In view of the effects of the -receptor blocking brokers on coronary blood flow, it seems paradoxical that these medicine are useful for the prophylactic treatment of 11 Adrenoceptor Antagonists one hundred fifteen angina pectoris, a condition characterized by inadequate myocardial perfusion. The chief good thing about the blockers in this condition derives from their capability to decrease cardiac work and oxygen demand. The capability of -blockers to decrease cardiac work and oxygen demand may also be liable for the favorable effects of these brokers in the long-term management of congestive coronary heart failure. The launch of renin from the juxtaglomerular cells of the kidney is believed to be regulated partially by receptors; most -blockers decrease renin launch. The glycogenolytic and lipolytic actions of endogenous catecholamines are mediated by -receptors and are topic to blockade by -blockers. This metabolic antagonism exerted by the -blockers is particularly pronounced if the levels of circulating catecholamines have been increased reflexively in response to hypoglycemia. Other physiological adjustments induced by hypoglycemia, such as tachycardia, could additionally be blunted by blockers. These agents therefore must be used with caution in sufferers prone to hypoglycemia. Because the metabolic responses to catecholamines are mediated by 2-receptors and presumably by 3-receptors, 1-selective antagonists corresponding to metoprolol and atenolol could additionally be better selections every time -blocker remedy is indicated for a patient who has hypoglycemia. Propranolol increases airway resistance by antagonizing 2-receptor�mediated bronchodilation. The cardioselective -blockers produce much less bronchoconstriction than do the nonselective antagonists. The mechanism is believed to be associated to a decreased production of aqueous humor. Other therapeutic applications of the -blockers are discussed later in the chapter. Hyperthyroidism the -blockers considerably cut back the peripheral manifestations of hyperthyroidism, significantly elevated heart fee, elevated cardiac output, and muscle tremors. Although the -blockers can improve the medical status of the hyperthyroid affected person, the affected person remains biochemically hyperthyroid. They are most logically employed within the administration of hyperthyroid disaster, in the preoperative preparation for thyroidectomy, and in the course of the preliminary period of administration of specific antithyroid medicine (see Chapter 65). Glaucoma -Blockers can be utilized topically to cut back intraocular strain in sufferers with continual open-angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension. The mechanism by which ocular pressure is lowered seems to depend on decreased production of aqueous humor. Timolol has a considerably greater ocular hypotensive effect than do the available cholinomimetic or adrenomimetic medicine. The -blockers are also helpful within the treatment of acute angle-closure glaucoma. Anxiety States Patients with anxiousness have quite a lot of psychic and somatic signs. Migraine the -blockers may provide some value within the prophylaxis of migraine headache, probably because a blockade of craniovascular -receptors leads to decreased vasodilation. The painful phase of a migraine attack is believed to be produced by vasodilation. Clinical Uses the -receptor blocking agents have widespread and essential uses within the management of cardiac arrhythmias, angina pectoris, and hypertension.
Dipyridamole 100 mg online
Some of those are directly appearing amines that must work together with adrenoceptors to produce a response in effector tissues blood pressure ranges for young adults purchase 100 mg dipyridamole with visa. Some directly performing compounds blood pressure and dehydration quality dipyridamole 100 mg, similar to phenylephrine and methoxamine, activate -adrenoceptors virtually solely, whereas others, like albuterol and terbutaline, are practically pure adrenoceptor agonists. Drugs that exert their pharmacological actions by releasing norepinephrine from its neuronal shops (indirectly acting) produce effects that are just like these of norepinephrine. They are probably to exert strong -adrenoceptor exercise, but 1-adrenoceptor activity typical of norepinephrine, corresponding to myocardial stimulation, also occurs. Some of the not directly acting adrenomimetic amines are used primarily for their vasoconstrictive properties. Many noncatecholamine adrenomimetic amines resist enzymatic destruction, have prolonged actions, and are orally efficient. The indirectly acting drugs are efficient only when given in giant doses, they usually often produce tachyphylaxis. In dentistry, phenylephrine is used to prolong the effectiveness of a local anesthetic. Dobutamine exerts a larger effect on the contractile force of the center relative to its effect on the heart fee than does dopamine. Dobutamine increases the oxygen calls for on the guts to a lesser extent than does dopamine. Like dopamine, though at larger doses, it produces vasodilation of renal and mesenteric blood vessels. Dobutamine could additionally be more helpful than dopamine in the remedy of cardiogenic shock. Terbutaline and Albuterol Terbutaline and albuterol are relatively selective 2adrenoceptor agonists. Terbutaline and albuterol are successfully administered both orally or subcutaneously. Therapeutically, terbutaline and albuterol are used to treat bronchial bronchial asthma and bronchospasm related to bronchitis and emphysema (see Chapter 39). Side results embrace nervousness, tremor, tachycardia, palpitations, headache, nausea, vomiting, and sweating. The frequency of look of these adverse effects is minimized, nevertheless, when the drugs are given by inhalation. Directly Acting Adrenomimetic Drugs Phenylephrine, Metaraminol, and Methoxamine these medication are instantly appearing adrenomimetic amines that exert their results primarily by way of an motion on -adrenoceptors. All three drugs enhance each systolic and diastolic blood pressures via their vasoconstrictor motion. The pressor response is accompanied by reflex bradycardia, no change within the contractile force of the heart, and little change in cardiac output. Consequently, their length of action is significantly longer than that of norepinephrine. Following intravenous injection, pressor responses to phenylephrine could persist for 20 minutes, while pressor responses to metaraminol and methoxamine might last for more than 60 minutes. The clinical uses of those drugs are associated with their potent vasoconstrictor motion. They are used to restore or maintain blood stress throughout spinal anesthesia and sure other hypotensive states. The reflex bradycardia induced by their rapid intravenous injection has been used to terminate assaults of paroxysmal atrial tachycardia. The latter effects are primarily as a result of its indirect actions and rely largely on the discharge of norepinephrine. However, ephedrine may cause some direct receptor stimulation, notably in its bronchodilating results. Unlike epinephrine or norepinephrine, however, ephedrine is efficient when administered orally. Pharmacological Actions Ephedrine increases systolic and diastolic blood stress; coronary heart fee is generally not elevated. Ephedrine produces bronchial easy muscle rest of extended duration when administered orally. Clinical Uses Ephedrine is beneficial in relieving bronchoconstriction and mucosal congestion associated with bronchial bronchial asthma, asthmatic bronchitis, continual bronchitis, and bronchial spasms. It is commonly used prophylactically to forestall asthmatic assaults and is used as a nasal decongestant, as a mydriatic, and in certain allergic disorders. Although its bronchodilator motion is weaker than that of isoproterenol, its oral effectiveness and extended duration of motion make it priceless in the treatment of those circumstances. Because of their oral effectiveness and larger bronchiolar selectivity, terbutaline and albuterol are replacing ephedrine for bronchodilation. Tachycardia, untimely systoles, Amphetamine Amphetamine is an not directly performing adrenomimetic amine that relies upon for its action on the release of norepinephrine from noradrenergic nerves. Both systolic and diastolic blood pressures are elevated by oral dosing with amphetamine. It has been used within the therapy of weight problems due to its anorexic effect, though tolerance to this impact develops quickly. Amphetamine is no longer really helpful for these uses due to its potential for abuse. Amphetamine is beneficial in sure instances of narcolepsy or minimal mind dysfunction. Epinephrine given in small therapeutic doses (A) Increases systolic blood stress through 2 receptor stimulation in the left ventricle (B) Decreases heart fee reflexively. When phenylephrine is administered by sluggish infusion of the therapeutic dose, which is the more than likely impact illustrated in the following desk: improve ; lower ; no change (0) Phentolamine blocks -adrenoceptors, permitting parasympathetic nerves innervating the sphincter muscle to take over. This results in a much less opposed contraction of the sphincter muscle induced by transmitter acetylcholine and a constriction of the pupil or miosis. The depressor effect of small doses is due to greater sensitivity to epinephrine of vasodilator 2-adrenoceptors than of constrictor -adrenoceptors and a dominant action on 2-adrenoceptors of vessels in skeletal muscle. Amphetamine is an indirectly acting adrenomimetic amine that depends on the discharge of norepinephrine from noradrenergic nerves for its action. Thus, its effect depends on neuronal uptake (blocked by cocaine) to displace norepinephrine from the vesicles and the supply of norepinephrine (depleted by reserpine). The main cardiovascular response to this drug is an increase in blood pressure associated with reflex bradycardia. He has a household history of cardiovascular disease, having lost each his father and grandfather earlier than both reached age 60. He has just lately observed decreased vitality, particularly during exercise, and had symptoms (difficulty in respiration, chest pain) that took him to the emergency division.
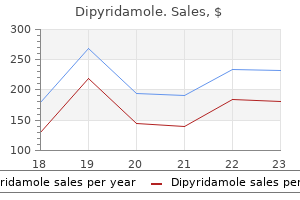
Purchase dipyridamole 100 mg online
These hypersegmented neutrophils can be a sign of vitamin deficiencies hypertension nursing teaching 25 mg dipyridamole discount visa, specifically B12 and folate heart attack ekg dipyridamole 100 mg buy free shipping. The classic pathway is activated when C1 recognizes and binds the fixed fragment of both IgG or IgM in an antigen-antibody advanced. The various pathway is triggered when activated C3 or IgA antibodies recognize antigens on microbial surfaces. The three activation pathways converge on the generation of C3 convertase, an enzyme that continues to be related to the pathogen surface to set off cleavage of other complement proteins. C3 convertase breaks down C3 molecules to the enzymatically energetic C3b and the anaphylatoxin C3a, which mediates a local inflammatory response. Binding of C3b to C3 convertase creates C5 convertase, which cleaves C5 into C5a (another anaphylatoxin) and C5b, which is inserted into the cell membrane of the pathogen. As with the coagulation system, the formation of some lively enzymes can lead to rapid activation and amplification of the complement cascade. Therefore, regulatory proteins are essential in sustaining management of the cascade. Adaptive Immunity Adaptive immunity can be divided into cell-mediated immunity and humoral immunity. They are involved in cell-mediated immunity and have two main obligations (Table 3-6). Helper T cells (Th): "Help" B cells produce antibodies and secrete cytokines that "assist" other cells carry out their capabilities. Their primary perform is to recognize extracellular pathogens and differentiate into plasma cells that produce antibodies to goal pathogens for elimination from the physique. Antibodies Antibodies are proteins composed of two heavy (H) chains and two light (L) chains. Antibodies are composed of two antigen-binding fragments (Fab) and one fixed fragment (Fc). Antibodies have four major features: Opsonization: the Fab portion of immunoglobulin, significantly IgG, binds to microbial surfaces. The other facet of the antibody, the Fc portion, binds to cell surface receptors on the phagocytes, permitting phagocytosis. Neutralization: Binding to microbial surfaces can forestall adherence to and infection of host tissues. Complement activation: Binding of IgG or IgM to antigens prompts the complement system, leading to phagocytosis, anaphylaxis, and cytolysis. In this way, B cells can produce antibodies with different amino acid sequences, and thus different antigen specificities. Random combos of heavy and light chains: the differentially spliced heavyand light-chain genes must then combine to form a practical antibody molecule. Through circulate cytometry, lymphocytes and other cells may be separated primarily based on their cell surface parts. This is beneficial when attempting to rely the variety of T or B lymphocytes in a patient or determining the extent of differentiation of a population of cells (eg, when evaluating for immunodeficiency or lymphoid cancers). The B cell then differentiates, undergoes isotype class switching, affinity maturation, after which becomes both a memory B cell or a plasma cell particular to a single isotype. This permits passing cells to identify what kinds of proteins are being made and degraded in that cell. Skin autografts are used when transferring healthy skin to a burned or broken location on the identical particular person. Syngeneic grafts (isografts): A switch of tissue between genetically identical members of the same species, corresponding to between equivalent twins. Allografts (homografts): Transfer of tissue between genetically different members of the identical species. The physique can bear transplant rejection in a variety of ways, as offered in Table 3-9. T Cells Mature T cells specific totally different proteins that help identify them and the operate they serve. This interplay is an important costimulatory sign for B cells, stimulating differentiation and isotype switching. Cytokines Cytokines are intercellular communication signals that are crucial in immune system operate. This results in the production of varied immunoglobulin isotypes through modifications within the constant area of heavy-chain genes. Two indicators are required for T-cell activation: Signal 1 (primary signal) and Signal 2 (costimulatory signal). Summary Immune cells and the molecules they specific or secrete are considerably interconnected to form a coordinated, environment friendly immune response to pathogens. These cells have to be eliminated by one of the mechanisms mentioned under to prevent autoimmune disease. Clonal deletion: A T cell that binds repeatedly (eg, because of a excessive concentration of self-antigen) undergoes programmed cell dying. Active suppression: Self-reactive T cells are saved nonfunctional when self-antigen is offered at low levels. The cells reacting at low ranges differentiate into regulatory cells, which secrete regulatory cytokines to prevent different cells from reacting to that antigen. B Cells Clonal Deletion B cells that react with self-antigen can either be deleted or endure receptor enhancing of the sunshine chain throughout their growth within the bone marrow. Receptor modifying changes the antigen specificity of the cell with the objective of stopping recognition and binding to self-proteins. Anergy Sometimes self-reactive B cells escape deletion and are by accident launched to the periphery. Clonal Ignorance Some B cells bind only weakly to self-antigen and so escape detection and deletion. These B cells are often nonfunctional (since their binding is weak), but can become activated if the concentration of their antigen is unusually excessive. Table 3-12 summarizes the key factors related to every and permits for comparison between the 2. In basic, an effective vaccine must provide a number of years of protection, though a quantity of doses (boosters) could also be necessary. Effective vaccines stimulate the production of neutralizing antibodies or induce cell-mediated immunity. Toxoid vaccines include inactivated toxins isolated from the microorganisms that produce them. Recombinant vaccines contain engineered protein elements that may stimulate manufacturing of protective antibodies to a pathogen.
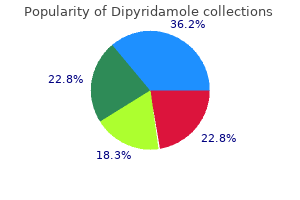
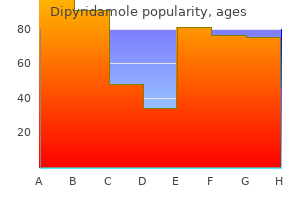
Purchase 100 mg dipyridamole with amex
If nitroprusside is run for a number of days blood pressure yahoo health 100 mg dipyridamole cheap otc, thiocyanate ranges must be monitored prehypertension to treat or not to treat buy dipyridamole 100 mg visa. This is completed in 4 ways: (1) by lowering the variety of impulses touring within the sympathetic nerves, (2) by inhibiting neurotransmitter launch, (3) by depleting the stores of norepinephrine, and (4) by antagonizing the actions of norepinephrine on effector cells. The websites of motion of those medicine are numerous and may finest be appreciated by contemplating the sympathetic arc concerned with blood strain regulation. These medication have numerous scientific uses, including treatment of cardiac arrhythmias (see Chapter 10) and angina pectoris (see Chapter 17), for which their therapeutic profit is directly associated to the blockade of -receptors within the myocardium. Unopposed -mediated responses can be expected to improve, rather than decrease, blood strain. Nevertheless, -blockers have proved to be quite efficient antihypertensive brokers, and so they have an important place in the treatment of primary hypertension. Decreases in coronary heart fee and cardiac output are the obvious outcomes of administration of -blockers. The discount of blood strain that happens in chronic treatment correlates finest with modifications in peripheral vascular resistance somewhat than with a drug-induced variation in coronary heart price or cardiac output. The reduction in plasma quantity produced by blockers contrasts with the elevated volume seen with other forms of antihypertensives. Tolerance to the antihypertensive actions of -blockers due to this fact is less of an issue than with the vasodilating drugs. An extra distinction from the vasodilators is that plasma renin activity is lowered, somewhat than increased, by propranolol (Inderal). When used alone over a quantity of weeks, -blockers produce a significant reduction in blood pressure in approximately 30% of patients with gentle to reasonable hypertension. Thus, -blockers can be employed as a first step in the management of hypertension. The combination of a -blocker, thiazide diuretic, and vasodilator offers vital management of moderate to extreme hypertension in approximately 80% of patients. From a hemodynamic viewpoint, there are several apparent benefits to utilizing a -blocker together with a vasodilator. Reflex-mediated cardiac stimulation is a typical characteristic of vasodilator therapy and can severely restrict its antihypertensive effectiveness. A -blocker will cut back the cardiac stimulation and thus protect the effectiveness of the vasodilator. Conversely, the vasodilator will forestall the increase in peripheral vascular resistance that occurs on initiation of treatment with a -blocker. Furthermore, vasodilator therapy initiates reflexes that result in a rise in plasma renin exercise. Thus, -blockers, similar to propranolol, that reduce plasma renin exercise are of obvious value. Although the -blockers are well-tolerated medication and patient compliance is nice, there may be issues with their administration, notably in sufferers with decompensated hearts and cardiac conductance disturbances. These potential problems and the antagonistic impact of -blockers are described intimately in Chapter eleven. The contraction of vascular clean muscle because of sympathetic nerve stimulation is thereby reduced, and blood pressure decreases. Guanethidine exerts its results at peripheral sympathetic nerve endings following its lively transport into the nerve varicosities by the neuronal amine transport system. This is identical uptake system that transports norepinephrine into the varicosity (see Chapter 9). The accumulation of guanethidine in adrenergic neurons, via an as yet unexplained mechanism, disrupts the method by which motion potentials set off the discharge of saved norepinephrine and different cotransmitters from nerve terminals. Guanethidine is appropriate for oral use, and that is its usual route of administration. The half-life of guanethidine is 5 days, with about one-seventh of the whole administered dose eliminated per day. The slow elimination contributes to the cumulative and extended effects of the drug. Guanethidine reduces blood stress by its ability to diminish vascular tone; both the arterial and venous sides of the circulatory system are concerned. The ensuing venous pooling contributes to orthostatic hypotension, a distinguished function of guanethidine treatment. The discount in blood strain is more prominent when the affected person is standing than recumbent. With the attainable exception of minoxidil, guanethidine is essentially the most potent orally efficient antihypertensive drug. Symptoms of unopposed parasympathetic activity embody such gastrointestinal disturbances as diarrhea and elevated gastric secretion. Guanethidine may aggravate congestive heart failure or really precipitate failure in patients with marginal cardiac reserve, owing to its ability to produce vascular volume growth, edema, and a reduced effectiveness of sympathetic cardiac stimulation. Guanethidine is contraindicated in sufferers with pheochromocytoma as a end result of the drug might release catecholamines from the tumor. Conversely, guanethidine competitively inhibits the uptake of medication which might be substrates for neuronal uptake, such because the not directly performing adrenomimetics, or sympathomimetics (see Chapter 10). Reserpine lowers blood stress by reducing norepinephrine concentrations within the noradrenergic nerves in such a method that much less norepinephrine is launched during neuron activation. Under normal circumstances, when an motion potential invades the sympathetic nerve terminal, a portion of the launched norepinephrine is recycled. In addition to impairing norepinephrine storage and thereby enhancing its catabolism, reserpine impairs the vesicular uptake of dopamine, the instant precursor of norepinephrine. Since dopamine should be taken up into the adrenergic vesicles to endure hydroxylation and type norepinephrine, reserpine administration impairs norepinephrine synthesis. The combined effects of the blockade of dopamine and norepinephrine vesicular uptake lead to transmitter depletion. Reserpine also interferes with the neuronal storage of a wide range of central transmitter amines such that significant depletion of norepinephrine, dopamine, and 5hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) happens. The depletion of mind amines also may contribute to the antihypertensive effects of reserpine. As with other sympathetic depressant medication, tolerance to the antihypertensive results of reserpine can occur, owing to a compensatory enhance in blood volume that regularly accompanies decreased peripheral vascular resistance. Because of its sedative properties, reserpine provides special benefit to hypertensive sufferers who exhibit symptoms of agitated psychotic states and who could also be unable to tolerate remedy with phenothiazine derivatives. Sedation and despair are the commonest, although nightmares and thoughts of suicide also occur. Reserpine treatment, due to this fact, is contraindicated in patients with a historical past of severe melancholy. Peripheral nervous system unwanted facet effects are the outcomes of a reserpine-induced reduction of sympathetic perform and unopposed parasympathetic exercise; symptoms include nasal congestion, postural hypotension, diarrhea, bradycardia, elevated gastric secretion, and occasionally impotence.

Cheap dipyridamole 100 mg fast delivery
Their uses in these circumstances are reviewed in Chapters 16 blood pressure medication makes me tired 25 mg dipyridamole with visa, 17 hypertension and diabetes 25 mg dipyridamole discount otc, and 20, respectively. However, they can be life threatening for a affected person with congestive heart failure. Caution have to be exercised in the use of -blockers in obstructive airway disease, since these medicine promote further bronchoconstriction. Cardioselective -blockers have less propensity to irritate bronchoconstriction than do nonselective -blockers. The use of -blockers in hypoglycemic sufferers is due to this fact harmful and have to be undertaken with warning. Whenever -blocker remedy is employed, the interval of best hazard for asthmatics or insulindependent diabetics is through the initial period of drug administration, since the best disruption of the autonomic steadiness will happen at this time. After high doses, patients may have hallucinations, nightmares, insomnia, and despair. Topical software of timolol to the attention is well tolerated, and the incidence of unwanted effects, which encompass burning or dryness of the eyes, is reported to be 5 to 10%. In spite of the potential seriousness of a few of their side effects, -blockers as a category are properly tolerated and affected person compliance is nice. Like certain different dolol and timolol), labetalol possesses a point of intrinsic activity. This intrinsic exercise, or partial agonism, especially at 2-receptors within the vasculature, has been suggested to contribute to the vasodilator effect of the drug. The membrane-stabilizing effect, or local anesthetic motion, of propranolol and a variety of other different blockers, is also possessed by labetalol, and in reality the drug is a fairly potent native anesthetic. The drug also has some intrinsic activity at -receptors, although this motion is lower than its intrinsic -receptor�stimulating results. Labetalol seems to produce leisure of vascular clean muscle not only by -blockade but also by a partial agonist effect at 2-receptors. In addition, labetalol may produce vascular leisure by a direct non�receptor-mediated impact. Labetalol can block the neuronal uptake of norepinephrine and other catecholamines. This motion, plus its slight intrinsic activity at -receptors, could account for the seemingly paradoxical, though infrequent, improve in blood stress seen on its initial administration. Absorption, Metabolism, and Excretion Labetalol is nearly utterly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. While traces of unchanged labetalol are recovered within the urine, many of the drug is metabolized to inactive glucuronide conjugates. The plasma half-life of labetalol is 6 to 8 hours, and the elimination kinetics are primarily unchanged in sufferers with impaired renal failure. These results range from particular person to particular person and rely upon the sympathetic and parasympathetic tone at the time of drug administration. The commonest hemodynamic effect of acutely administered labetalol in people is a decrease in peripheral vascular resistance and blood pressure without an appreciable alteration in heart rate or cardiac output. Labetalol (Normodyne, Trandate) possesses each blocking and -blocking activity and is approximately one-third as potent as propranolol as a -blocker and one-tenth as potent as phentolamine as an -blocker. Thus the drug may be most conveniently thought of as a -blocker with some -blocking properties. Acute administration of a -blocker produces a decrease in coronary heart price and cardiac output with little effect on blood stress, whereas acute administration of an blocker leads to a lower in peripheral vascular resistance and a reflexively initiated enhance in cardiac price and output. Generally, nonetheless, the decrease in coronary heart price is much less pronounced than after administration of propranolol or different -blockers. Labetalol, as a result of it possesses both - and -blocking activity, is helpful for the preoperative management of patients with a pheochromocytoma. Adverse Effects There have been stories of excessive hypotension and paradoxical pressor effects following intravenous administration of labetalol. These latter effects could also be as a outcome of a labetalol-induced blockade of neuronal amine uptake, which increases the concentrations of norepinephrine in the neighborhood of its receptors. Approximately 5% of the patients who obtain labetalol complain of side effects typical of noradrenergic nervous system suppression. These embrace postural hypotension, gastrointestinal distress, tiredness, sexual dysfunction, and tingling of the scalp. Side effects related to -blockade, corresponding to induction of bronchospasm and congestive heart failure, may also occur, however generally at a lower frequency than -receptor�associated results. Skin rashes have been reported, as has a rise within the titer of antinuclear antibodies. Despite the latter observation, the looks of a systemic lupus syndrome is uncommon. Labetalol additionally has been reported to intrude with chemical measurements of catecholamines and metabolites. Clinical Uses Labetalol is useful for the persistent treatment of main hypertension. It can be used alone however is extra usually employed together with different antihypertensive agents. Labetalol additionally has been used intravenously for the therapy of hypertensive emergencies. Like typical -blockers, labetalol may be helpful for patients with coexisting hypertension and anginal ache due to ischemia. It is also being investigated as a attainable therapeutic modality for ischemic coronary heart disease, even in the absence of hypertension. The profit derives from its -blocking activity, which decreases cardiac work, and from its capability to decrease afterload by virtue of its -blocking exercise. Other Compounds Several other -adrenoceptor antagonists, much like labetalol, exhibit a point of -receptor antagonism. Which of the next actions of epinephrine can be antagonized by prazosin but not by propranolol Which of the next adrenoceptor antagonists will cut back responses mediated by both - and receptors Shown is the impact of making use of norepinephrine on the arterial strain of an isolated (in vitro) section of artery from an experimental animal earlier than and after adding drug X to the tissue. Drug X is most likely: (A) Guanethidine (B) Propranolol (C) Cocaine (D) Prazosin (E) Atropine 5. Shown are dose�response curves for isoproterenol (control) each alone and within the presence of one or the opposite of two -receptor antagonists, drugs X and Y. The responses being measured are a rise in heart price of a human topic and rest of an in vitro strip of human bronchiolar smooth muscle. The adrenoceptors that epinephrine acts on to affect coronary heart price, renin release, bronchiolar tone, and glycogenolysis are -receptors. The radial clean muscle within the iris has -receptors that when activated, contract the radial muscle which dilates the pupil. Propranolol and metoprolol are selective for receptors, whereas prazosin and phenoxybenzamine are selective for -receptors.
Dipyridamole 100 mg free shipping
Drug Interactions the salicylates displace a number of medicine from plasma protein binding websites blood pressure goals 2015 generic dipyridamole 25 mg with visa, thereby resulting in arrhythmia unborn baby cheap 25 mg dipyridamole mastercard potential antagonistic effects by these agents. Since aspirin is an over-thecounter treatment, patients might fail to inform the doctor of their aspirin consumption. Anticoagulants are potentiated by aspirin by (1) displacement of the anticoagulants from plasma proteins and (2) the intrinsic anticoagulant impact of aspirin. Thus, the dosage of medication similar to coumarin and heparin should be decreased in patients taking aspirin. A related impact is noticed in patients taking oral sulfonylureas (Orinase, DiaBeta) for non�insulin-dependent diabetes or phenytoin (Dilantin) for seizures. Aspirin enhances the effects of insulin (leading to hypoglycemia), penicillins and sulfonamides (increasing acute toxicity), and corticosteroids. Aspirin will increase the hypotensive effects of the cardiac drug nitroglycerin however decreases the effectiveness of the loop diuretics. In patients taking methotrexate for cancer chemotherapy, aspirin could increase retention of the drug, and severe toxicity could outcome. Phenobarbital, often used for seizures, induces liver enzymes that improve the metabolism and excretion of aspirin, -adrenoceptor� blocking medication, corresponding to propranolol, and decrease the antiinflammatory effects of aspirin, whereas reserpine decreases its analgesic results. It can be not helpful as an antithrombotic agent within the prevention of myocardial infarction or transient ischemic attacks. Adverse Effects, Contraindications, and Drug Interactions Toxicity from overdose with acetaminophen differs in time course and mechanism from that observed with the salicylates. The onset of toxicity may not occur for several days, and the predominant injury is to the liver. The preliminary indicators of toxicity occur inside 12 to 24 hours and include nausea and vomiting. In addition to hepatotoxic effects, renal necrosis and myocardial damage may happen. Oral Nacetylcysteine is used to deal with acetaminophen toxicity, though many sufferers are hypersensitive to such remedy. In addition, gastric lavage with activated charcoal can be used immediately after ingestion of the drug to lower acetaminophen absorption from the stomach. Acetaminophen is contraindicated in late-stage alcoholism, since chronic alcohol consumption can induce the P450 system, leading to elevated manufacturing of the toxic metabolite of acetaminophen, hence to liver necrosis. In addition, barbiturates and phenytoin induce the liver P450 system and may lower the effectiveness of acetaminophen. Acetaminophen crosses the placenta but is nonetheless used in pregnant women with few side effects for the mother or the fetus. Although the drug has been shown to be present in breast milk, no conclusive evidence links the drug to abnormalities related to consumption of breast milk by the new child. Absorption is almost full following oral administration but varies with suppository forms of the drug. Acetaminophen is less plasma protein certain than the salicylates, though the amount bound varies from 20 to 50%. Following the use of regular therapeutic doses of acetaminophen, metabolism and conjugation to sulfate or glucuronides occurs, and clearance of those metabolites occurs within the kidney. A minor toxic metabolite is generated by the metabolism of acetaminophen via the P450 mixed-function oxidase system. This poisonous metabolite is often conjugated to glutathione within the liver and excreted through the kidney as conjugated cysteine and mercapturic acid. However, with the depletion of glutathione in certain illness states, corresponding to liver cirrhosis and necrosis, and following chronic use of excessive doses of acetaminophen, this toxic reactive metabolite can accumulate and induce liver harm. Indoles (indomethacin) and Related Compounds Chemistry and Mechanism of Action Indomethacin (Indocin) is an acetic acid by-product associated functionally to sulindac (Clinoril), a prodrug with an extended half-life, and etodolac (Lodine). The antipyretic ef- 26 Opioid and Nonopioid Analgesics 315 bile and through the kidney. Clinical Uses, Adverse Effects, and Contraindications All of those drugs produce analgesic effects, antipyresis, and antiinflammatory results. Indomethacin is useful within the remedy of acute gout, osteoarthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, and acceleration of the closure of the ductus arteriosus in premature infants. The tocolytic effects of indomethacin to prevent preterm labor are the result of its effects on prostaglandin synthesis. However, the toxicity of the drug limits such utility, because it increases fetal morbidity. The principal differences amongst these medicine lie in the time to onset and duration of motion. Naproxen has a long half-life, whereas fenoprofen and ketoprofen have short half-lives. All of the medicine are extensively metabolized within the liver and require enough kidney operate for clearance of the metabolites. The drugs vary in plasma protein binding, but clearly all are certain to a comparatively high diploma and can intrude with the binding of other drugs that compete for plasma protein binding (as described for aspirin). Clinical Uses, Adverse Effects, and Contraindications the arylpropionic acid derivatives are useful for the remedy of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis, for reduction of mild to moderate ache and fever, and for ache related to dysmenorrhea. Side effects of the medication are similar to but much less severe than these described for the salicylates. The concurrent use of ibuprofen with aspirin reduces the antiinflammatory effects of each medicine. Ibuprofen is contraindicated in sufferers with aspirin sensitivity resulting in bronchiolar constriction and in patients with angioedema. They are analgesic, antipyretic, and antiinflammatory brokers indicated for mild to reasonable ache, therapy of dysmenorrhea, rheumatoid arthritis, and osteoarthritis. These medication are metabolized by way of glucuronidation within the liver and excreted via the kidney. Thus, fenamates require normal liver and kidney function for excretion and are contraindicated in patients with both liver or renal failure. Overdose with fenamates results in seizures which are generally insensitive to traditional therapy with benzodiazepines. In cases of overdose with meclofenamate dialysis may be required to restore fluid and electrolyte steadiness. Their use is accompanied by serious opposed reactions, corresponding to anemia, nephritis, renal failure or necrosis, and liver injury. Interactions with numerous other drugs Arylpropionic Acid Derivatives Chemistry and Mechanism of Action Ibuprofen (Advil), flurbiprofen (Ansaid), fenoprofen (Nalfon), ketoprofen (Orudis), and naproxen (Naprosyn) are all 2-substituted propionic acid derivatives. The drug is contraindicated in kids and within the aged with diminished renal perform. The consequences of overdose happen slowly and may embody liver harm, renal failure, and shock. Supportive measures embrace air flow, dialysis, and gastric lavage with activated charcoal, in addition to the use of benzodiazepines to control convulsions.
Purchase dipyridamole 25 mg with visa
Active transport of the launched transmitter into effector cells (extraneuronal uptake) adopted by enzymatic inactivation by catechol-O-methyltransferase hypertension 360 mg purchase dipyridamole 100 mg free shipping. The neuronal transport system is crucial mechanism for eradicating norepinephrine blood pressure chart south africa 100 mg dipyridamole quality. Any norepinephrine or epinephrine within the circulation will equilibrate with the junctional extracellular fluid and thus turn out to be accessible each to the receptors and to neuronal transport. Thus, neuronal transport can also be an necessary mechanism for limiting the impact and period of action of norepinephrine or epinephrine, whether these are launched from the adrenal medulla or are administered as drugs. Neuronal uptake is primarily a mechanism for removing norepinephrine quite than conserving it. Under most circumstances, synthesis of recent norepinephrine is type of capable of maintaining with the wants of transmission, even within the full absence of neuronal reuptake. Neuronal transport happens from the junctional extracellular fluid (biophase) across the cell membrane of the neuron and into the neuronal cytosol. Vesicular transport is from the neuronal cytosol across the membrane of the vesicle and into the vesicle. Although these two techniques readily transport each norepinephrine and epinephrine, sure medicine will selectively inhibit one or the other transport system. The second most essential mechanism for removing norepinephrine from the synapse is the escape of neuronally released norepinephrine into the general circulation and its metabolism within the liver. This response reduces the organic activity of norepinephrine or epinephrine no much less than 100-fold. The listing of its substrates is very giant, including endogenous substances (norepinephrine, epinephrine, dopamine, tyramine, 5-hydroxy-tryptamine) and many medicine which are amines. The two varieties are differentiated on the premise of substrate and inhibitor specificity. The bigger portion, nevertheless, is metabolized and the products of metabolism excreted within the urine, often as conjugates. Measurements of norepinephrine, epinephrine, and their metabolites within the urine constitute valuable diagnostic aids, particularly within the detection of tumors that synthesize and secrete norepinephrine and epinephrine. The combined processes of extraneuronal uptake and O-methylation are believed to be a minor but functionally vital, website of irreversible loss of catecholamines. The respective receptors are called the muscarinic and nicotinic cholinoreceptors or the muscarinic and nicotinic receptors of acetylcholine. The motion of acetylcholine on the skeletal muscle motor finish plate resembles that produced by nicotine. However, these receptors are sufficiently chemically various that totally different exogenous agonists and antagonists can distinguish amongst them. Great therapeutic profit has been obtained from this diversity as a result of it permits the event of therapeutic agents that may selectively mimic or antagonize actions of acetylcholine. Such a variety of receptor subtypes exists for other neurotransmitters along with acetylcholine. Adrenoceptors interact not solely with norepinephrine but also with the adrenal medullary hormone epinephrine and a variety of chemically associated medicine. However, the responses produced by the drugs in different autonomic buildings differ quantitatively or qualitatively from one another. On the premise of the noticed selectivity of action among agonists and antagonists, it was proposed that two kinds of adrenoceptors exist. Subsequently, it has turn into necessary to classify the adrenoceptors additional into 1-, 2-, 1-, and 2-receptor subtypes. The 1-adrenoceptors are located at postjunctional (postsynaptic) websites on tissues innervated by adrenergic neurons. The 1-adrenoceptors are discovered mainly within the coronary heart and adipose tissue, whereas 2-adrenoceptors are positioned in numerous sites, including bronchial smooth muscle and skeletal muscle blood vessels, and are associated with easy muscle relaxation. Activation of 1-adrenoceptors in clean muscle of blood vessels leads to vasoconstriction, whereas activation of 2-adrenoceptors in blood vessels of skeletal muscle produces vasodilation. Activation of 1-adrenoceptors on cardiac tissue produces an increase within the coronary heart price and contractile pressure. Norepinephrine and epinephrine are potent adrenoceptor agonists, while isoproterenol, an artificial Cholinoceptors the action of administered acetylcholine on effector systems innervated by parasympathetic postganglionic neurons (smooth muscle cells, cardiac muscle cells, and exocrine gland cells) resembled the actions produced by the naturally occurring plant alkaloid muscarine. The actions of each acetylcholine and muscarine on the visceral effectors are similar to those produced by parasympathetic nerve stimulation. Furthermore, the results of acetylcholine, muscarine, and parasympathetic nerve stimulation on visceral effectors are antagonized by atropine, another plant alkaloid. The administration of acetylcholine mimics the stimulatory impact of nicotine, the alkaloid from the tobacco plant, on autonomic ganglia and the adrenal medulla. Norepinephrine and epinephrine are thus potent vasoconstrictors of vascular beds that contain predominantly -adrenoceptors, while isoproterenol has little effect in these vessels. Isoproterenol and epinephrine are potent 2adrenoceptor agonists; norepinephrine is a relatively weak 2-adrenoceptor agonist. Isoproterenol, epinephrine, and norepinephrine are potent 1-adrenoceptor agonists; thus, all three can stimulate the heart (Table 9. The existence of a 3-adrenoceptor has lately been demonstrated in human adipose tissue together with the 1-adrenoceptor. This remark raises the likelihood that eventually therapeutic medicine may selectively alter lipid metabolism and subsequently provide therapeutic management of weight problems. The 3-receptor and the lately recognized subtypes inside the 1- and 2-receptor teams (1A, 1B, etc. One exception is tamsulosin, an antagonist with some selectivity for 1Areceptors within the urinary tract. Presynaptic Receptors Presynaptic or prejunctional receptors are situated on the presynaptic nerve endings and function to control the quantity of transmitter released per nerve impulse and in some cases to have an result on the rate of transmitter synthesis by way of some as yet undetermined feedback mechanism. For occasion, throughout repetitive nerve stimulation, when the concentration of transmitter launched into the synaptic or junctional cleft is comparatively excessive, the released transmitter could activate presynaptic receptors and thereby reduce the further launch of transmitter. Such an action could prevent excessive and extended stimulation of the postsynaptic cell. In this case, the activation of the presynaptic receptor can be part of a unfavorable suggestions mechanism. The presynaptic receptors may have pharmacological significance, since several drugs may act partially both by stopping the transmitter from reaching the presynaptic receptor, thus inflicting excessive transmitter launch, or by immediately stimulating presynaptic receptors and thereby diminishing the amount of transmitter launched per impulse. The inhibitory presynaptic -adrenoceptors found on noradrenergic neurons are of the 2-subtype. Adrenoceptors of the 2 subclass additionally happen presynaptically, and activation of these receptors leads to enhanced norepinephrine release. These and many different medication that alter transmission are mentioned in subsequent chapters.
Buy generic dipyridamole 100 mg online
The monosaccharides are absorbed via transporters and carried to the liver via the portal vein prehypertension 120 80 dipyridamole 25 mg amex. Glycolysis Function Initial step in the metabolism of glucose to produce energy for the cell arteria3d urban decay city pack 100 mg dipyridamole generic overnight delivery. Glycolysis normally happens in cardio environments, but can occur beneath anaerobic conditions. Phosphorylation of glucose to glucose-6-phosphate (G6P) blocks its ability to diffuse across the cell membrane, trapping it within the cell. Serum lactic acid levels are measured in clinical scenarios when hypoperfusion (shock) is suspected. Hexokinase: Ubiquitous, nonspecific (phosphorylates many different six-carbon sugars), low Km (easily saturable), feedback inhibited by G6P. Glucokinase: Mainly in the liver, very particular for glucose, high Km (not easily saturable), feedback inhibited by fructose-6-phosphate (F6P, the product of the subsequent step in glycolysis). Pyruvate kinase deficien y is the second most common (9% of all cases) and results in hemolysis. For instance, eating fava beans can precipitate assaults of hemolysis, a syndrome referred to as favism. Because this is an X-linked recessive dysfunction, the vast majority of patients shall be male. When mitochondrial injury happens, cytochrome c leaks out, a key sign for initiating apoptosis. The second, reversible, step isomerizes the sugars so they can reenter glycolysis. Ribulose-5-phosphate: Nucleotide synthesis, F6P, glyceraldehyde-3phosphate (glycolysis intermediate). This creates a pH gradient throughout the internal mitochondrial membrane (intermembrane area more acidic, ie, decrease pH, and matrix much less acidic with a better pH). Dietary sucrose is broken down by sucrase within the small gut to fructose and glucose. Glyceraldehyde is phosphorylated by triose kinase, also creating glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate, which enters glycolysis. Therefore, basic galactosemia presents in newborns, versus fructose intolerance, which presents at the time of weaning. Deficiencies in fructokinase are benign, leading to fructosuria (essential fructosuria). Fructose-1-phosphate aldolase deficiency leads to hereditary fructose intolerance, characterized by extreme hypoglycemia upon sucrose or fructose ingestion. Galactose Metabolism Function Converts dietary galactose (from lactose) to a form that can enter glycolysis. Genetic mutations in kinases, such as fructokinase and galactokinase, subsequently lead to illnesses in which sugars can freely enter and exit cells, and due to this fact spill out into the urine. This invariably leads to extra severe clinical disease-leading to a general precept: In issues of fructose and galactose metabolism, mutations in enzymes additional alongside the pathway cause far more severe ailments. Dietary lactose is damaged down within the small intestine by lactase to galactose and glucose. This happens in the lens of the eye, resulting in osmotic damage, and early cataract formation in this disease. This is a severe illness leading to failure to thrive and increased risk for E coli sepsis (a crucial association for Step 1). Because the same pathway is blocked, just one step later, sufferers even have cataracts, and generally are born with them. Management requires elimination of galactose and lactose (the disaccharide consisting of glucose and galactose) from the food regimen. Anaerobic Metabolism and Cori Cycle Function Shuttles lactate from muscle into the liver, permitting muscle to function anaerobically when energy necessities exceed oxygen consumption. Hypoxic muscle cells perform anaerobic glycolysis, producing lactate, which leaks into the blood. The liver converts this metabolic waste back into pyruvate, a substrate for gluconeogenesis. Therefore, any compound that can be converted into pyruvate may be built-in right into a glucose molecule via gluconeogenesis and is therefore stated to be glucogenic. This whole paradigm is the explanation starvation will trigger muscle loss: When dietary intake is insufficient to assist the blood glucose, muscle tissue begin to break sarcomeric proteins into amino acids, transmitting them to the liver for conversion by way of gluconeogenesis into glucose to stave off hypoglycemia (and lack of consciousness). This further burst of blood glucose is meant to enable for survival until the following meal. Hypoglycemia triggers a catabolic state, pushed by counter-regulatory hormones, including epinephrine and glucagon. These activate lipolysis, releasing free fatty acids, that are subsequently transformed to ketone our bodies within the liver. Glycogen Metabolism Function Helps keep glucose homeostasis by forming (glycogenesis) or breaking down (glycogenolysis) glycogen. Pyruvate is a remarkably versatile metabolite that could be shunted into quite a few different biochemical pathways, including the Cahill cycle (1), gluconeogenesis (2), tricarboxylic acid cycle (2 and 3), in addition to anaerobic glycolysis and the Cori cycle (4). To enhance storage efficiency, branch points are added by branching enzymes to allow for a extra compact three-dimensional structure. Serves to shield from hypoglycemia in periods of starvation or between meals. Debranching enzymes have to be used to untangle the branches of glycogen created during glycogen synthesis. All end in irregular glycogen metabolism and an accumulation of glycogen inside cells. As a result, fructose-1-phosphate accumulates after fructose consumption, depleting hepatocytes of phosphate. They must keep away from foods with both fructose and sucrose, because sucrose is simply a disaccharide composed of glucose and fructose. Glycolysis has three irreversible steps (catalyzed by hexokinase, phosphofructokinase, and pyruvate kinase). Gluconeogenesis makes use of 4 separate enzymes to bypass these unilateral steps, as proven with solid purple arrows. These extra enzymes are solely produced in the kidney, liver, and gut, hence these are the one tissues which are in a place to manufacture glucose during occasions of hunger (ie, to perform gluconeogenesis). This free ammonium is subsequently incorporated into urea, which is excreted into the urine. Location the urea cycle is a dialog between the mitochondria and cytoplasm of liver cells. The stress hormones glucagon and epinephrine ultimately induce glycogen breakdown in order that glucose can be obtained for immediate use. Insulin, a hormone launched after meals, causes liver cells to polymerize glucose into glycogen to prepare for future intervals of hunger. Pathophysiology Disorders of the urea cycle contain enzymatic deficiencies that prevent detoxing of ammonia from protein catabolism into urea. Therefore, the finding that unites all of them is hyperammonemia that worsens with excessive protein consumption.
Real Experiences: Customer Reviews on Dipyridamole
Gambal, 49 years: The Treponema genus consists of venereal treponema (T pallidum, subspecies pallidum (simply referred to as T pallidum) in addition to nonvenereal treponema that cause numerous infections such as yaws, pinta, and bejel. Because the metabolic responses to catecholamines are mediated by 2-receptors and presumably by 3-receptors, 1-selective antagonists such as metoprolol and atenolol may be better decisions every time -blocker remedy is indicated for a affected person who has hypoglycemia.
Grobock, 46 years: The antihypertensive drug diazoxide is certainly one of the few examples of therapeutically helpful noncompetitive antagonists (see Chapter 20). Cimetidine, propoxyphene, and isoniazid even have been reported to inhibit metabolism of carbamazepine.
Kulak, 28 years: This system plays an necessary position within the regulation of blood strain and vascular tone. Tolerance and Dependence Tolerance to stimulants develops fairly rapidly, even within the therapeutic dose vary.
Flint, 33 years: These brokers gained considerable consideration as a outcome of their increased efficiency Study Questions 1. It is used solely by the intravenous route for the therapy of hypertensive emergencies.
Xardas, 27 years: The fibrinolytic enzyme system and its function within the etiology of thromboembolic disease. The second stage of illness usually includes the development of telangiectasias, pores and skin atrophy, mottled irregular pigmentation, and other traits of poikiloderma.
Gembak, 40 years: These undesirable effects could be managed by concurrent therapy with a -blocker and a diuretic. It is used to elevate dopamine levels within the neostriatum of parkinsonian patients.
9 of 10 - Review by Y. Asam
Votes: 144 votes
Total customer reviews: 144