Famvir dosages: 250 mg
Famvir packs: 10 pills, 20 pills, 30 pills, 60 pills
250 mg famvir order fast delivery
Porphyria with jaundice hiv infection diagram buy 250 mg famvir fast delivery, extreme chronic hemolytic anemia starting within the neonatal period hiv infection kidney disease discount 250 mg famvir visa, hepatosplenomegaly, and photosensitivity. Up to 80% of sufferers with porphyria cutanea tarda have the sporadic type of the disease. It has been demonstrated that sporadic porphyria cutanea tarda is a multifactorial dysfunction involving a mix of genetic and environmental components. Iron catalyzes the formation of reactive oxygen species and this will likely enhance uroporphyrin formation by rising the rate at which uroporphyrinogen is oxidized to uroporphyrin, resulting in the manifestations of the illness. Whatever the mechanism, the iron overload has essential therapeutic implications as venesection can induce a remission. Hereditary coproporphyria Clinical features this very rare autosomal dominant type of porphyria develops on account of a deficiency of coproporphyrinogen oxidase. Biochemical evidence of liver involvement is common, however medical manifestations are unusual. Hepatoerythropoietic porphyria Clinical options hepatoerythropoietic porphyria may be very uncommon and, in reality, represents the homozygous form of familial porphyria cutanea tarda. Variegate porphyria is associated with diminished exercise of protoporphyrinogen oxidase, the penultimate enzyme within the heme biosynthetic pathway. In gentle disease the deposits are delicate and are usually limited to the papillary dermal capillaries, but in more severe circumstances the deposits are widespread, occur more deeply in the dermis, and provides the vessel partitions a attribute. In addition, finely fibrillar materials is often present each around the vessels and on the epidermal basement membrane area. Neutrophil polymorphs showing leukocytoclasis have been described in acute lesions of erythropoietic protoporphyria and pink cell extravasation is sometimes evident. Most typically, however, as proven by antigen mapping experiments, blistering commences in the lamina lucida. Ultrastructural research counsel that these bodies characterize a combination of degenerating keratinocytes, colloid our bodies, and basement membrane fragments formed by repeated blistering and re-epithelialization. Its distinction from the dermal modifications of scleroderma could also be very troublesome, nevertheless it has been stated that the texture of the collagen bundles is considerably looser in porphyria. Centrofacial papular lymphangiectasis is characterised by the presence of dilated lymphatics within the superficial dermis. Direct immunofluorescence reveals Ig (usually IgG, IgM, and sometimes Iga) with C3 around the superficial vasculature in a donut distribution and as a nice granular deposit on the epidermal basement membrane region. On electron microscopic examination, the airplane of cleavage is variable: in some it has been shown to be inside the lamina lucida, whereas in others it has been deep to the lamina densa. More recent genome-wide affiliation studies have rapidly expanded the information of different genetic defects answerable for the disease. Many sufferers current initially with acute irritation of the primary metatarsophalangeal joint (podagra). More commonly, in major gout, renal stones are a function, and continual urate nephropathy (due to deposition of monosodium urate monohydrate salt crystals within the interstitial tissues of the kidney), presenting as delicate proteinuria and hypertension, often develops. In secondarily infected lesions, a neutrophil polymorph infiltrate is usually present. Exogenous ochronosis Clinical options Deposition within the skin of an equivalent pigment to that seen in alkaptonuria may occur because of the appliance of phenol (carbolic acid) to leg ulcers, remedy with resorcinol and picric acid, the oral and intramuscular administration of antimalarials such as chloroquine, and the appliance to dark skin of bleaching creams containing hydroquinone, most frequently in black women. In addition to causing ochronosis, hydroquinones containing bleaching lotions have been shown to be carcinogenic in rodents. Spinal involvement results in disc herniation, spondylosis, and osteophytosis with resultant limitation of motion and lack of peak. Cardiovascular involvement occurs in as a lot as 50% of sufferers and mainly consists of pigmentation and calcification of the aortic valve, which can result in stenosis. Ochronotic pigmentation is regularly seen in the hyaline cartilage of the larynx, trachea, and bronchi. The lesions developed as a consequence of the appliance of hydroquinone bleaching cream. Pellagra the pigment shaped has not been characterized however there are some similarities to melanin. With chronicity, large amorphous eosinophilic granules could develop, resembling colloid milium. Hartnup illness Clinical features hartnup disease is an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by faulty gastrointestinal absorption and renal reabsorption of monoamine and monocarboxylic amino acids due to a defect within the neutral brush border system. In addition to a pellagra eruption (see below), patients even have a attribute aminoaciduria and cerebellar ataxia. Pellagra Clinical features pellagra develops as a consequence of deficiency of nicotinic acid (niacin, vitamin B3) or its precursor tryptophan. Other options typically present embody cheilosis, glossitis, angular stomatitis, and oral or perianal sores. Neurological involvement evolves, with headache, depression, and ataxia initially and extra extreme symptoms of disorientation, delirium, and coma and eventually demise. Differential analysis the prognosis may be very much dependent upon clinicopathological correlation, particularly in those cases that resemble necrolytic migratory erythema and acrodermatitis enteropathica. Scurvy Clinical options Scurvy, as a end result of vitamin C deficiency, outcomes from a food plan inadequate in recent fruit and greens and is nowadays most frequently encountered following inappropriate dieting, meals fads, and in alcoholics and socially isolated people. It may also be secondary to consuming boiled or evaporated milk which is poor in vitamin C. Calcinosis cutis Calcinosis cutis might happen when connective tissue is irregular (dystrophic) or the place calcium or phosphate ranges in the blood are high (metastatic); alternatively, there may be no obvious underlying trigger (idiopathic) (Table 13. Under this variant, iatrogenic calcinosis cutis induced by native application of chemical substances or medicines is also included. In the localized form of dystrophic calcinosis cutis, the underlying anomaly may be inflammatory or traumatic in nature, for instance acne scars, burns, fat necrosis or subcutaneous and intramuscular injections. Calcification might occur in lots of adnexal tumors, for instance pilomatrixoma and trichoepithelioma. Localized dystrophic calcification with bone formation has additionally been described in combined connective tissue illness. Scleroderma, particularly the CreSt variant, tends to present localized deposition of calcium, significantly on the digits and over bony prominences. Metastatic calcinosis cutis Clinical options Metastatic calcification happens because of hypercalcemia or hyperphosphatemia as could also be seen in continual renal failure, hyperparathyroidism, and sarcoidosis. In the skin, the clinical appearances are of exhausting nodules and plaques, which can ulcerate to liberate chalky material and ultimately go away a scar. Vascular calcification with thrombosis may lead to livedo reticularis, ulceration, and gangrene, significantly affecting the hands, fingers, toes, and lower legs (so-called scientific calciphylaxis). Calcification complicating discoid lupus erythematosus and subacute lupus erythematosus is restricted to a number of case stories. Lesions are most common on the scalp, neck, preauricular space, and palms, and usually have a tendency to develop in patients with sclerodermoid illness. Some circumstances may represent dermatomyositis during which the acute part was not identified. Pathogenesis and histological features Calcium stains blue with hematoxylin and eosin.
Garden Chervil (Chervil). Famvir.
- Dosing considerations for Chervil.
- What is Chervil?
- Cough, digestive disorders, high blood pressure, eczema, gout, abscesses, and other conditions.
- How does Chervil work?
- Are there safety concerns?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96274
Cheap 250 mg famvir visa
Lateral and inferiorly directed branches provide a half of the piriform cortex and uncus of the temporal lobe throat infection symptoms of hiv order famvir 250 mg visa. Medially directed branches enter the midbrain to provide part of the center third of the cerebral peduncle hiv infection rates in australia order famvir 250 mg fast delivery, which contains the corticospinal fibers. A distal group of branches supplies the inferior half of the posterior limb of the interior capsule, retrolenticular fibers of the inner capsule, and the hilum of the lateral geniculate body. These distal branches anastomose with tributaries from the lateral choroidal branch of the posterior cerebral artery. The plexal segment begins the place this vessel enters the supracornual recess of the temporal horn, and provides the plexus only in the temporal horn, but might occasionally provide the complete plexus within the temporal horn and atrium. The dimension and extension of distribution is in equilibrium with the posterior choroidal branches of the homolateral posterior cerebral artery. A few branches of the posterior choroidal artery could arise from the anterior choroidal artery, which shall be larger. Branches of the posterior cerebral artery might come up from the anterior choroidal artery and feed that territory. The anterior speaking artery is normally single but could additionally be duplicated or triplicated. Several small branches might come up from the anterior communicating artery to the infundibulum, chiasm, and preoptic areas of the hypothalamus. Occasionally, the anterior center cerebral artery or median artery of the corpus callosum could also be encountered. Pericallosal Artery It is the portion of the most important anterior cerebral artery complicated distal to the anterior communicating artery. The artery ascends in front of the lamina terminalis, between the 2 hemispheres alongside the longitudinal fissure, making a curve Chapter 2 Arteries of the Head and Neck thirteen around the genus of the corpus callosum in the pericallosal cistern. Ascends in front of the lamina terminalis to the extent of the genu of the corpus callosum. Lies in the pericallosal cistern and passes backward towards the splenium, typically following the upper surface of the corpus callosum. The posterior length of the pericallosal artery is decided by the scale of the callosomarginal artery and the posterior pericallosal department of the posterior cerebral artery. Sometimes the posterior pericallosal department could be the terminal portion of the pericallosal artery and, due to this fact, not originate from the posterior cerebral artery. Several massive cortical branches arise from the convexity of the pericallosal artery to provide the white matter of the medial part of the orbital gyri, the gyrus rectus, the olfactory bulb and tract, the medial surface, and a strip of the lateral floor of the frontal and parietal lobes. Multiple small branches arising from the concavity of the pericallosal artery provide the corpus callosum, septum pellucidum, and columns of the fornix. Usually arises from the infracallosal section of the pericallosal artery or from a typical trunk that also offers rise to the frontopolar artery. The forward course of the orbital artery lies within the medial or inferior surface of the frontal lobe, and provides the medial basal region of the frontal lobe, together with the gyrus rectus, the medial part of the medial gyri and the olfactory bulb and tract. Usually the second department of the pericallosal artery, arising from the infracallosal segment. It could arise as a typical trunk with the frontobasilar artery or from the callosomarginal artery. This artery passes in an anterior path alongside the medial surface of the brain hemisphere describing a mild curve in the course of the frontal pole to provide the anterior portion of the medial and lateral surfaces of the superior frontal gyrus. It could also be a single vessel or a group of a quantity of ascending vessels arising from the pericallosal artery. When this branch is a single trunk it follows a course roughly parallel to that of the pericallosal artery. The branches of the callosomarginal artery ascend on the medial surface of the hemisphere and proceed to the lateral convexity for about 2 cm, supplying premotor, motor, and sensory areas. Branches Anterior Internal Frontal Artery Middle Internal Frontal Artery Posterior Internal Frontal Artery Paracentral Artery Cortical Branches of the Anterior Cerebral Artery Eight territories of vascular supply are identified regarding the cortical branches of the anterior cerebral artery. The medial floor supplied by the anterior cerebral artery is compartmentalized by several named sulci or fissures. The subfrontal sulcus is fixed and situated on the inferior restrict of the superior frontal gyrus. Superior to the subfrontal sulcus is the big superior frontal gyrus, which is subdivided by many inconstant and unnamed sulci. The paracentral sulcus marks the posterior limit of the superior frontal gyrus and the limit between it and the paracentral lobule. The paracentral lobule is variable in dimension and is split from above by the central sulcus, which extends from the lateral surface of the hemisphere. The marginal limit of the cingulate sulcus separates the paracentral lobule from the precuneus, or quadrilateral lobe, which is bounded inferiorly by the subparietal sulcus and posteriorly by the parietooccipital fissure. The cortical arteries arise from either the pericallosal artery or a marginal trunk of the pericallosal artery. The dimension of the pericallosal artery varies inversely with that of the callosomarginal trunk. It arises independently from the pericallosal artery, within the majority of the cases, and should share a standard origin with the frontopolar artery or is a branch of a callosomarginal trunk together with two or more different cortical branches. There are anastomoses with the orbitofrontal branch of the middle cerebral artery within the 14 Atlas of Vascular Anatomy area of the H-shaped sulcus. In lateral views of angiograms this branch initiatives on the level or beneath the extent of the ophthalmic artery. May share a typical origin with another cortical branch, except the inner parietal artery. In three fourths of the cerebral hemisphere it presents as a single artery dividing into two or more branches. The artery supplies the anterior third of the interior floor of the superior frontal gyrus. Less incessantly arises from the callosomarginal trunk, together with the other inner frontal arteries. Courses in the marginal limb of the cingulate sulcus however could sometimes run in the paracentral sulcus. Supplies the paracentral lobule and sends a branch from the medial floor of the brain in the central sulcus. This territory extends posteriorly to embody roughly 80% of the precuneus, the place the artery anastomoses with the parieto-occipital branches of the posterior cerebral artery. An accessory middle cerebral artery may be found in about 3% of cases, under the bifurcation of the interior carotid artery. More not often the accent middle cerebral artery could originate from the anterior cerebral artery, and its embryologic origin is more doubtless to be associated to the artery of Heubner.
Buy famvir 250 mg online
Dermoscopy permits the location most affected by alopecia over the scalp to be chosen for the biopsy hiv infection without ejaculation buy cheap famvir 250 mg. If these are high the supply should be determined primary hiv infection symptoms rash famvir 250 mg cheap free shipping, particularly with respect to the presence of an ovarian tumor or adrenal hyperplasia. Confusion with telogen effluvium is possible however distinction is straightforward, primarily based on the reality that telogen effluvium is generalized and androgenetic alopecia is localized. Young ladies and men with this condition have greater levels of 5-reductase and androgen receptor in frontal hair follicles when compared with occipital follicles. It would appear that the telogen hair follicle follows an alternate route, one not adopted by a new early anagen however somewhat finishing off for a prolonged time frame with an empty follicle. In the deeper sections, hair bulbs are current at completely different depths, and focally they might be fully absent, solely follicular stellae remaining. In late androgenic alopecia the stellae turns into abnormally thick and could impede the growth of the follicle. It is necessary, nonetheless, to observe that both diseases might current concurrently and that continual telogen effluvium might uncover occult androgenetic alopecia. Below are sections from an space of frontal alopecia with more than half of the follicles miniaturized (vellus) or in the strategy of miniaturization. The follicular models have disappeared and within the subcutaneous fat there are abundant stellae. In basic, the histological appearance is very related to that of a normal skin biopsy. Differential diagnosis the most important differential diagnoses are diseases which present with diffuse nonscarring alopecia together with telogen effluvium, alopecia areata, and trichotillomania. In the part on the level of the subcutaneous fat (right) most of the follicles have been changed by follicular stellae (S); (B) follicular unit with two terminal follicles at the bottom and three miniaturized follicles at the prime; (C) miniaturized follicle (vellus hair). B Differential diagnosis the differential diagnosis includes other causes of circumscribed non-scarring alopecia, significantly alopecia areata and tinea capitis. It is extra common in people between 15 and forty years of age and about 60% of instances happen earlier than the age of 20. When these patches extend and turn into confluent, involving the entire scalp, the appearance is called alopecia totalis. In the periphery of the patches of alopecia one typically finds exclamation mark hairs, that are brief and become thinner as they gradually method the scalp. In this superior stage connective tissue has nearly fully replaced follicular constructions and the appearances resemble a scarring alopecia. One terminal hair follicle is present on the right aspect of the sphere (unaffected scalp). Spontaneous remission can be anticipated in 34�50% of patients within 1 yr, though nearly all will experience multiple episode of the disease. Severity of alopecia areata at time of first consultation and response to therapy is a crucial prognostic issue. Since neurotrophins and their receptors are differentially expressed in subsets of immune cells in alopecia areata, a task for these proteins in the pathogenesis appears doubtless. It has been proposed that expression of alopecia areata involves a complex interplay of multiple genes, in which main genes control susceptibility to the illness while other minor ones modify the phenotype. It is necessary to keep in thoughts that the histopathological features depend on the stage of the illness. In each specific affected space the established lesion is observed in the middle of the patch of alopecia and the extra active options are evident on the edge adjoining to the traditional scalp. Late stage In the late stage of the illness, the inflammation decreases and numerous miniaturized hair follicles and telogen follicles are current. Such hairs are found within the middle or upper dermis and have been described as nanogen. In vertical sections the proximal end of the hair shaft acquires a ragged look rather than the traditional membership shape. In longstanding alopecia areata the vast majority of the hair follicles are in catagen and telogen. Numerous stellae are present within the deep dermis and the subcutaneous tissue and these could also be accompanied by an inflammatory cell infiltrate and melanin pigment. In some cases there may be destruction of the hair follicle by the aforementioned infiltrate and histiocytes and large cells. In patients presenting with trachyonychia, a nail biopsy usually exhibits a lymphocytic infiltrate with exocytosis and spongiosis involving the proximal nail fold, nail matrix, nail mattress, and hyponychium. Early stages In the early stages of the illness there is a rise in the variety of catagen and telogen follicles. Following this, the follicle quickly returns to anagen and the cycle repeats itself. Due to this steady cycle and the accompanying Differential analysis the differential prognosis of alopecia areata is based on whether the scientific sample of hair loss is localized or diffuse. In instances with localized areas of hair loss, the differential diagnosis includes trichotillomania, triangular temporal alopecia, syphilis, discoid lupus erythematosus, lichen planopilaris, frontal fibrosing alopecia, pseudop�lade, and tinea capitis. Note (from left to right) that as the pili bulb disappears the infiltrate turns into much less dense. C could also be very comparable but clinically the plaques hardly ever show full absence of hairs. Discoid lupus erythematosus, lichen planopilaris, and frontal fibrosing alopecia show extra prominent irritation within the superior section of the follicle, and end in scarring alopecia with interface change and everlasting lack of terminal hair follicles. The lower frame reveals follicular stellae with lymphocyte infiltrate and pigment incontinence. A B lack of terminal hair follicles and a gentle inflammatory cell infiltrate localized to the upper phase of the follicle. Clinically, even in the most severe variants of alopecia totalis and alopecia universalis, small isolated clumps of hair are seen that allow distinction from telogen effluvium. In androgenetic alopecia, the histologic image could additionally be similar to that of persistent areata alopecia as within the former the miniaturization of hairs could additionally be very in depth. Nevertheless, the shortage of lymphoid infiltration and the totally different scientific image might help in the differential diagnosis. Hair follicles within the subcutaneous tissue with a lymphocyte infiltrate of variable depth. For this cause, an intensive interview and detailed psychiatric history are usually required. If potential, this area ought to be chosen in order that adjacent hairs may hide the shaved space. Histological options the histological features of trichotillomania are quite distinct and, with medical correlation, enable the analysis to be made in the majority of instances. Many sections should be examined as a end result of just a few sections might show the attribute adjustments. Nonscarring alopecias at scanning magnification essentially the most salient features are a really excessive percentage of catagen or telogen follicles, a variety of regular follicles, and an absence of inflammation. The follicle in the backside of the sphere is in catagen and has lost its internal root sheath and exhibits intense yellow keratinization (elastic tissue stain).
Buy 250 mg famvir otc
The anterior department provides the anterior portion of the choroid plexus of the temporal horn of the ventricles hiv infection rates in north america discount 250 mg famvir overnight delivery, whereas the posterior branch supplies the choroid plexus of the trigone and lateral ventricle antiviral compounds buy famvir 250 mg lowest price. The lateral choroidal artery additionally provides the crus, commissure, physique, and part of the anterior columns of the fornix and thalamus. The size of this vessel is often inversely proportional to the dimensions of the anterior choroidal artery. There are anastomoses between branches of this artery with branches of posteromedial and anterior choroidal arteries. The distal vessels may anastomose with branches of the calcarine artery within the posterior third of the calcarine fissure. Parieto-Occipital Artery May come up independently from the posterior cerebral artery on the level of the ambient cistern. It may also originate with the calcarine artery from the bifurcation of the posterior cerebral trunk in the proximal third of the calcarine fissure. This artery originates from the quadrigeminal segment in 22% and more distally in 40% of cases. Branches include lateral posterior choroidal arteries, and branches to the hippocampus, pulvinar, and medial and lateral geniculate bodies. The major trunk of the parieto-occipital artery often divides into a variety of cortical branches that supply the medial portion of the parieto-occipital lobe, precuneus, and deep into the parieto-occipital fissure. On the lateral view of an arteriogram the parieto-occipital branches course posteriorly and superiorly because the uppermost of the three posterior cortical branches of the posterior cerebral artery. In the frontal projection the proximal parietooccipital artery is usually probably the most medial of the three posterior cortical branches as it surrounds the medial face of the parieto-occipital lobe. Calcarine Artery Arises on the bifurcation of the principle posterior cerebral trunk in the rostral third of the calcarine sulcus. Hippocampal Branches the arteries to the hippocampus originate from the trunk of the posterior cerebral artery near the origin of the lateral choroidal arteries. Meningeal Branches the meningeal branches are small and come up from the peduncular phase of the posterior cerebral artery. They course around the midbrain and supply the midline strip of the inferior surface of the tentorium reverse to the junction of the falx cerebri with the tentorium. It may come up from the posterior cerebral artery or from the lateral choroidal artery or from the posterior temporal artery. This artery passes across the splenium, operating anteriorly throughout the supracallosal cistern and anastomosing with the distal branches of the anterior pericallosal artery. On the left, the vertebral artery originates from the arch between the left frequent carotid and left subclavian arteries in about 2. In that case the vertebral artery enters the foramen of the transverse strategy of the fifth cervical vertebra, as a substitute of the sixth cervical vertebra as ordinary. Other variations similar to origin of the left vertebral artery distal to the left subclavian artery or from the left frequent carotid artery or exterior carotid artery are extremely uncommon. The proper vertebral artery originating from the proper common carotid artery or the aortic arch is present in less than 1% of circumstances. Anterior Temporal Artery Arises as a single trunk or as multiple branches from the proximal ambient section of the posterior cerebral artery. Runs lateral and anterior under the hippocampal gyrus supplying the inferior aspect of the anterior portion of the temporal lobe. There are anastomoses with the anterior temporal branches of the center cerebral artery. Posterior Temporal Artery Arises from the midambient phase of the posterior cerebral artery as a single trunk in 80% of circumstances. Several small branches originate from this Chapter 2 Arteries of the Head and Neck 19 a left dominant artery is more frequent. In cases of occlusion of the left subclavian artery, a steal phenomenon develops with enlargement of the right and left vertebral arteries and inversion of the circulate within the left vertebral artery. There is also reversal of the move within the posterior brain circulation causing lack of steadiness or collapse, particularly when heavy exercise is performed with the left arm. The occlusion of the best subclavian artery and steal phenomenon related to the right arm is less widespread. Muscular Branches In each cervical space the vertebral artery sends a radicular department, following the ventral (anteriorly) and dorsal (posteriorly) nervous roots, and muscular branches creating an anastomotic network with muscular branches from the deep cervical artery, occipital artery (posteriorly), ascending cervical artery, and ascending pharyngeal artery (anteriorly). The anastomoses create a longitudinal vascular axis by the connection of the three vertical axis (anteriorly created by the ascending cervical artery and ascending pharyngeal artery, in the middle by the vertebral artery, and posteriorly by the deep cervical artery and occipital artery). Together with the muscular and radicular branches, some branches give origin to the adjacent meninges. Some of the radicular branches give origin to the radiculomedullary branches (anterior or posterior). Segments of the Vertebral Artery the primary phase of the vertebral artery extends from the origin to its level of entrance into the foramen of the transverse course of (usually) of the sixth cervical vertebra (in 87. It is surrounded by the cervical sympathetic nerve plexus and is said anteriorly to the vertebral and jugular vein and the inferior thyroid artery. The second phase courses cranially by way of the foramina of the transverse processes till it reaches the transverse strategy of the axis. The artery is in close contact medially with the uncinate means of the vertebral physique and posteriorly with the ventral rami of the cervical nerves. The third phase extends from its exit at the axis to its entrance into the spinal canal. After leaving the transverse foramen of axis, it programs laterally and posteriorly to pass via the transverse foramen of the atlas. After passing the transverse foramen of the atlas, the artery runs posteromedially on the horizontal groove on the upper floor of the posterior arch of the atlas. When it approaches the midline, it turns cephalad and perforates the posterior atlanto-occipital membrane to enter the vertebral canal. At this stage, the persistence of the embryonic proatlantal intersegmental artery may lead to a uncommon however exuberant communication between the inner or exterior carotid arteries and the vertebral artery. The occipital artery may arise sometimes as a branch of the third section of the vertebral artery. The fourth phase of the vertebral artery perforates the dura and runs anteromedially by way of the foramen magnum. At this degree the artery lies in entrance of the medulla oblongata and joins the contralateral vertebral artery forming the basilar artery. Meningeal Branches Posterior Meningeal Branch Arises above the level of the arch of the atlas slightly below the foramen magnum. Supplies the medial portion of the dura of the posterior fossa, as nicely as the falx cerebelli. It could arise from the posterior division of the ascending pharyngeal artery (neuromeningeal trunk). Anterior Meningeal Branch Originates from the distal part of the second phase of the vertebral artery.
Proven famvir 250 mg
Law enforcement ought to be in attendance during the examination of any suspect to guarantee the security of the examiner hiv infection icd 10 buy famvir 250 mg otc, the witness hiv infection from undetectable discount famvir 250 mg with visa, and the cooperation of the suspect. The physical and evidentiary examination of the suspect is just like that of the sufferer. The main variations lie in historical past taking, reference samples, and more "blind" samples. During the examination of a suspect, legislation enforcement officers, rather than the suspect, provide the historical past of the event. Previously recommended, head and pubic hair reference samples are now not required in most areas and practitioners should check with local protocols for guidance on this. Apply special consideration not only to nail scrapings but additionally to swabbing all the fingers for possible vaginal epithelial cells from digital penetration. With an unwashed penis, swabs virtually uniformly show evidence of female cells as a lot as 24 hours after coitus. Most frequent are alcohol, marijuana, cocaine, and benzodiazepines; others account for less than 5% of positive exams. The Unconscious Victim and "Drug-Facilitated Sexual Assault" Alcohol and other medicine play an important role in many sexual assaults. Popular media has raised public awareness of medicine used to facilitate sexual assault under the time period date-rape drugs (Box fifty eight. Forensic laboratories usually provide an evaluation for a number of medication in a selected check designed for the sexual assault sufferer. However, testing may not be adequately sensitive to take a look at for all substances used throughout drug-facilitated sexual assault. The drugs mostly associated with drug-facilitated sexual assault are ethanol, marijuana, cocaine, and benzodiazepines. A widespread state of affairs is for the victim to have one glass of wine (or another usual drink), abruptly really feel nauseated, after which get up hours later in a special location and missing intervening reminiscence. Some keep in mind quick segments of exercise that may point out some sort of sexual acts. A complete medical-forensic examination ought to be performed on these individuals. Obtain samples of both blood and urine, if possible, for toxicology (including ethanol), with actual occasions of assortment documented. Some forensic laboratories supply a "date-rape panel" that tests for a variety of commonly used substances. Extreme sensitivity have to be used when discussing positive genital findings with a victim who has no reminiscence of any sexual exercise. Many times, the imagined sexual acts can create just as severe a traumatic response as an precise remembered sexual assault. However, because the early Nineties, nurses or nurse clinicians have been performing an increasing variety of sexual assault examinations. The clinician has often completed extra intensive coaching on sexual assault examination (mean of eighty hours) and proof collection and, accordingly, might carry out a more comprehensive examination with better assortment of proof. Many involved feel that designated clinicians understand and think about the emotional wants of the victim more absolutely due to their further specialty coaching. A concise and complete well-documented chart usually negates the need for a clinician to appear in court docket. Once on the witness stand, the inspecting clinician is most often considered a percipient witness and not essentially an skilled within the space of sexual assault. Factual information in reply to questions should be given only if one knows the details; assumptions ought to be prevented. Statements such as "there have been marks on the body that have been consistent with chew marks" are preferable to statements such as "there have been chunk marks. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Web-based damage statistics question and reporting system [online], Atlanta, 2012�2013, National Center for Injury Prevention and Control, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. American College of Emergency Physicians: Evaluation and management of the sexually assaulted or sexually abused affected person, ed 2, Atlanta, 2013, u. Wawryk J, Odell M: Fluorescent identification of biological and other stains on skin by means of various light sources. Kamenev L, Leclercq M, Francois-Gerard C: Detection of p30 antigen in sexual assault case materials. Graves H, Sensabaugh G, Blake E: Postcoital detection of a male-specific semen protein. Trussell J, Rodriguez G, Ellerston G: updated estimates of the effectiveness of the yuzpe routine of emergency contraception. Resnick H: Prevention of post-rape psychopathology: preliminary findings of a managed acute rape therapy research. Smith K, Holmseth J, MacGregor M, et al: Sexual assault response group: overcoming obstacles to program improvement. Management of Increased Intracranial Pressure and Intracranial Shunts Alessandra Conforto and Jonathan G. Vasogenic edema outcomes from increased permeability of the capillaries, which leads to passage of excess fluid into the extracellular house. Cytotoxic edema is because of accumulation of intracellular fluid in brain tissue (neurons and glia) secondary to dysfunction of the adenosine triphosphatase pump. Brain tumors embody neoplasms that originate in the mind itself (primary mind tumors) or contain the mind as a metastatic web site (secondary brain tumors). Primary mind tumors embrace tumors of the brain parenchyma, meninges, cranial nerves, and other intracranial structures (the pituitary and pineal glands). Secondary brain tumors, the most typical sort, originate elsewhere within the physique and metastasize to the intracranial compartment. In some cases the accompanying clinical symptoms could additionally be vague or subtle and make analysis tough. The fixed-volume principle was supported by George Kellie a quantity of years later and have become often known as the Monro-Kellie doctrine. This doctrine has since guided our understanding of intracranial dynamics and the rules of autoregulation. A, Relationships of the assorted supratentorial compartments as seen in a coronal section. Obstructive hydrocephalus occurs when circulate is blocked at any level in the ventricular system by clotted blood, tumor, colloid cyst, edema, or major stenosis. Communicating hydrocephalus is due to impedance of circulate beyond the ventricular system on the degree of the basal cisternae or lack of absorption by the arachnoid villi. Communicating hydrocephalus can occur with both an infection and subarachnoid hemorrhage. The lesion has exerted a mass effect on the brain causing 7 mm of midline shift (left arrow) and subsequent subfalcine herniation. A, Hyperdense blood from subarachnoid hemorrhage may be seen collecting in the basal cistern (arrow).
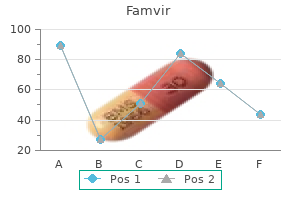
Order 250 mg famvir mastercard
The cortical venous drainage is primarily from the superficial sylvian vein (large brief arrow) hiv infection rates canada 250 mg famvir quality, draining to the cavernous sinus (open arrow) and to the pterygoid plexus (large arrowhead) through the bone by a large vein hiv infection transmission buy cheap famvir 250 mg. A, Venogram of the best inner jugular vein exhibits the dilation of the inferior bulb. Note the triangle shaped by the medial and lateral heads of the sternocleidomastoid muscle showing as a window for puncture and catheterization of the internal jugular vein. Computerized tomographic angiography of the neck exhibiting the anatomy of the internal jugular vein, the carotid artery, and the superficial muscular tissues. Shows the superficial tissues masking the right inside jugular vein and carotid. B, Deeper view of the gentle tissues of the right neck shows the exterior jugular vein and part of the proper facial vein and artery. C, the connection of the best carotid artery and inside jugular vein becomes extra apparent behind the sternocleidomastoid muscle. The bifurcation of the carotid is now seen and the external carotid artery is clearly delineated. F, Last picture shows the best inner jugular vein faintly and the right vertebral artery becomes seen. Schematic drawing of the anatomic relationship of the internal jugular veins and the frequent carotid artery, seen with the patient in the head-to-toe place, with the operator positioned on the head of the patient ready for inner jugular access. The distribution of the situation of the interior jugular vein in relation to the artery is given in a clock-dial configuration and percentages proven as seen in 188 sufferers who have been candidates for an inner jugular puncture. A, Selective injection into the inferior thyroid vein, filling retrograde partially the proper center thyroid vein. A, Anastomosis (asterisk) between the frontal vein (1), temporal vein (2), and superficial sylvian vein (3). B, Superior sagittal sinus (4), lateral sinus (transverse sinus) (5), sigmoid sinus (6), internal jugular veins (7), cavernous sinus (8). The superficial venous drainage is dominantly carried out by a vena of Labb� (large short arrow). The superficial brain drainage is predominantly by a vein of the Trolard type (large short arrow) with tributaries from the frontal lobe (arrowhead) and temporal (double arrowhead). Posterior caudal vein (small arrowhead) and anterior caudal vein (arrow) draining into the thalamostriate vein (double arrowhead). Lateral atrial vein (large arrowhead) draining into the basal vein of Rosenthal (double arrowhead). There are three medial atrial veins (small arrowheads); essentially the most anterior one is more medial within the frontal view, and the most posterior one is extra lateral in the frontal view. The anterior and posterior longitudinal caudal veins (arrowhead) drain to the inferior ventricular vein (large arrowhead) with typical curved sample. Petrous veins (small arrows), draining to the superior petrous sinus on the best (large brief arrow), cavernous sinus (large arrowhead), intercavernous sinus (large arrow). Schematic drawing of the anatomic relationships of the cavernous and inferior petrosal sinuses in axial view. Selective injection into the inferior petrosal sinuses displaying retrograde filling of the intercavernous sinuses and pterygoid plexus. T 4 Lymphatic System of the Head and Neck he lymph nodes of the top and neck comprise a terminal group and numerous intermediary groups. The terminal group is related to the carotid sheath and can additionally be called the deep cervical group. All the lymphatic vessels of the head and neck drain into the cervical group, immediately or indirectly. The efferents from the deep cervical lymph nodes comprise what known as the jugular trunk. In the neck Submandibular Lymph Nodes Submental Lymph Nodes Anterior Cervical Lymph Nodes Superficial Cervical Lymph Nodes Upper Deep Cervical Lymph Nodes these lymph nodes drain into the upper a part of the internal jugular vein. Efferents from this group move to the lower deep cervical group and prolong to the jugular trunk. These nodes are situated in entrance of the tragus or on the fascia of the parotid gland, and in addition drain the lymph from the eyelids and the pores and skin over the zygomatic bone area. The posterior side of the auricle and the scalp on the lateral aspect of the cranium drain to the upper deep cervical lymph nodes, and some part of it drains to the retroauricular group of lymph nodes. The retroauricular lymph nodes are superficial to the sternocleidomastoid attachment on the mastoid. The lobule of the auricle, the inferior meatus, and the pores and skin over the angle of the mandible are drained by vessels that go to the superficial cervical lymph nodes or to the upper deep cervical lymph nodes. The superficial cervical lymph nodes are positioned alongside the exterior jugular vein, superficial to the sternocleidomastoid. Some of the efferents of this group may be part of the upper deep cervical lymph nodes and some be part of the lower deep cervical lymph nodes. The occipital region is drained partly to the occipital group of lymph nodes and partly by a trunk alongside the posterior border of the sternocleidomastoid, which extends to the decrease deep cervical lymph nodes. Lymphatic Drainage of the Superficial Tissues of the Head and Neck There are several groups of lymph nodes involved with the drainage of the superficial tissues of the head and neck. Most of the superficial tissues are drained by lymphatic vessels that drain into the neighboring groups of nodes and the efferents of which drain into the deep cervical lymph nodes. The extra medial and inferior lymphatics comply with the course of the facial vein and terminate within the submandibular group of lymph nodes. The submandibular group of lymph nodes is located under the deep cervical fascia within the area of the submandibular gland. These nodes receive afferents from the submental, buccal, and lingual group of lymph nodes. The external nostril, cheek and higher lip, and lateral part of the lower lip drain to the submandibular nodes. The central part of the decrease lip, the ground of the mouth and the tip of the tongue drain to the submental group of lymph nodes. This group of lymph nodes is positioned on the mylohyoid between the anterior bellies of the 2 digastric muscular tissues. Lymphatic Drainage of the Nasal Cavity, Nasopharynx, and Middle Ear the lymphatic drainage of the anterior nasal cavity is through the vessels that drain the skin over the nostril to the submandibular nodes. The remaining nasal cavity, paranasal tissues, nasopharynx, and pharyngeal end of the auditory tube drain to the upper deep cervical nodes, immediately or by way of the retropharyngeal lymph nodes. Lymphatic Drainage of the Larynx, Trachea, and Thyroid Gland There is an upper and a lower group of lymph vessels at the larynx divided by the vocal fold. The cervical portion is drained to the pretracheal and paratracheal nodes, or directly to the nodes of the lower deep cervical group. Lymphatic Drainage of the Superficial Tissues of the Neck Many of the vessels draining the superficial tissues of the neck go to the higher or decrease deep cervical lymph nodes.
Syndromes
- Blood tests to check for signs of hantavirus
- Euphoria ("drunk" feeling)
- Change your workouts so that you are exercising within your ability.
- You will save money. If you smoke a pack a day, you spend around $1,800 a year on cigarettes.
- Excessive bleeding
- Is able to control the muscles used to urinate and have bowel movements (sphincter muscles), but may not be ready to use the toilet
Generic 250 mg famvir otc
On endoscopy hiv infection blood famvir 250 mg proven, the larynx confirmed thickened antiviral resistance mechanisms order famvir 250 mg online, purple, velvety, and edematous mucosa; the lips were thickened and fissured with angular cheilitis and fissured tongue. It is unclear whether this widespread involvement of the mucosa of the higher respiratory tract signifies a extra severe and extensive form of plasma cell gingivostomatitis. Direct immunofluorescence studies are often positive for the lupus band test in lesional tissue. Clinically, although the gingiva may be hyperplastic and edematous, gingivitis/periodontitis responds nicely to local remedy. Orofacial granulomatosis Clinical features Orofacial granulomatosis (cheilitis granulomatosa, granulomatous cheilitis) is a continual, non-necrotizing, granulomatous and inflammatory condition, doubtless a delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction. It is characterized by nontender swelling and edema of the lips and/or face, usually however not always accompanied by swelling of the gingiva (usually across the anterior teeth), and cobblestoning, folding, and erythema of the buccal mucosa. Of curiosity, sufferers with orofacial granulomatosis however no gastrointestinal symptoms had been found on ileocolonoscopy and biopsy to have intestinal pathology and granulomata in 54% of cases. Foreign materials throughout the granulomata successfully excludes a analysis of orofacial granulomatosis. Differential prognosis Granulomatous diseases associated with particular infections or foreign material should at all times be excluded. It presents as friable, fiery red, painful, eroded, denuded connected gingiva, totally on the facial or buccal facet, with occasional areas of ulceration. Desquamative gingivitis represents a definite medical manifestation of autoimmune blistering illnesses, hypersensitivity reactions or oral lichen planus. Cases of linear Iga confined to the mouth likely symbolize Iga kind mucous membrane pemphigoid. Unlike circumstances with ocular involvement, cicatrization is an uncommon finding and was famous in only 9% of instances in one series. Several subsets of mucous membrane pemphigoid exist, with variable antigenic characteristics however all are characterized by predominant involvement of the mucous membranes by a subepithelial blistering dysfunction. Direct immunofluorescence studies reveal basement membrane zone antibodies in a smooth, continuous linear fluorescence sample in 67�96% of cases. Indirect immunofluorescence studies in salt-split pores and skin reveal circulating IgG or Iga in 84�100% of cases. Direct immunofluorescence studies are essential in helping to differentiate between lichen planus and interface autoimmune stomatitides. Cases beforehand referred to as pure oral linear Iga illness ought to in all probability be reclassified as mucous membrane pemphigoid, Iga type. Lupus erythematosus 411 Pemphigus Clinical features Oral pemphigus vulgaris sometimes begins within the sixth decade of life with a female predilection. Direct immunofluorescence reveals deposition of IgG and/or complement in the intercellular space, and alongside the basement membrane zone. Direct immunofluorescence studies reveal homogeneous linear deposits of Iga alongside the basement membrane zone. It is believed that both dysregulation of the immune system caused by the neoplasm leads to manufacturing of autoantibodies or host antitumor response produces antibodies that cross-react with native antigens. Direct immunofluorescence studies reveal granular deposits of Iga in the basement membrane, significantly on the suggestions of the papillae. Direct immunofluorescence research present linear deposits of IgG and C3 at the basement membrane zone much like lesions of pemphigoid. Oral involvement � primarily within the type of ulcers, erythema with or without white striations, exfoliative areas, and discoid plaques � is seen in 26�45% of sufferers with systemic lupus erythematosus, presenting totally on the exhausting 412 Diseases of the oral mucosa palate, buccal mucosa, and lips. Histological features Oral lesions of both systemic and discoid lupus erythematosus exhibit hyperparakeratosis or hyperorthokeratosis, epithelial hyperplasia or atrophy, liquefactive degeneration of the basal cells, subepithelial paS-positive deposits, perivascular inflammatory infiltrates (with some cases showing a bandlike lichenoid infiltrate), and collagen degeneration. In some sufferers, the illness runs a protracted course limited to the upper airways earlier than progressing to multiorgan involvement. Oral mucosal biopsies present marked pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia with edema, a blended acute and chronic inflammatory cell infiltrate, hemorrhage, and vascular dilatation; many eosinophils may also be current. Granulomata are often poorly fashioned or absent although scattered multinucleated large cells are typically present. Other vasculitides also wants to be considered though sole presentation in the oral cavity is rare. Salivary duct cyst or sialocyst outcomes from dilatation of the excretory duct, caused by a distal obstruction. Salivary duct cyst or sialocyst results from dilatation of the excretory duct, attributable to a distal obstruction and is subsequently a retention cyst. Superficial mucoceles are distinctly vesicular or dewdrop-like, raising the suspicion of a herpetic an infection or autoimmune vesiculobullous disease and happen in older adults, notably on the palate, retromolar pad, and buccal mucosa. Differential analysis parulides (gum-boils) of the gingiva can typically be mistaken for extravasation mucoceles. Bacteria and inflammatory cells may be current between the calculus and the duct lining, or between lamellations. Necrotizing sialometaplasia Clinical options this is a self-healing inflammatory condition of salivary glands that may be clinically and histologically mistaken for a malignancy due to its quickly progressive ulcerative nature and the lack of related ache in a significant proportion of instances. It normally presents as a painful or painless ulcer or (less often) as a mass, with the majority (approximately 80%) occurring on the hard palate. Histological options the calculi have a lamellated appearance with alternating eosinophilic and basophilic bands and a usually homogeneous center. Such calculi typically reside inside a cystically dilated excretory duct that displays squamous metaplasia. Serous and mucoserous glands are much less likely to present the necrosis and infarctive adjustments. Differential diagnosis the preservation of lobular architecture, lack of infiltration of the encompassing tissues by the epithelial elements, infarction necrosis, and customarily bland nuclear morphology of the metaplastic islands distinguish this condition from squamous cell carcinoma. Mucoepidermoid carcinoma tends to have a considerable number of mucous cells and will typically present apparent infiltration of surrounding buildings. Nicotinic stomatitis Clinical options Nicotinic stomatitis (stomatitis nicotina) is related to pipe smoking and its severity is proportional to the duration of the behavior. Similar modifications have been described in patients who apply reverse smoking (smoking with the lighted finish of the cigarette in the mouth as is frequent in elements of asia). Pathogenesis and histological features the etiology is unknown but the situation is more likely to represent an inflammatory response to a wide selection of local irritants. Cases of carcinomatous transformation have occurred in older male patients with outside occupations and tobacco smoking; eversion of the decrease lip will increase its exposure to actinic harm. Differential diagnosis Similar histological modifications are seen in glandular obstruction such as occurs in glands draining right into a mucocele and, specifically, in glands that have been plugged by thick mucinous secretions or by small calculi, a common phenomenon in the higher lip. Lobules of minor salivary gland could also be current depending on the depth of the biopsy. Benign lesions are inclined to have a long history of gradual enlargement whereas malignant lesions are probably to grow extra rapidly and ulcerate.
250 mg famvir buy amex
It is always of value to use at least two markers for melanoma as very often S-100 protein unfavorable variants could additionally be encountered antiviral warning famvir 250 mg generic without a prescription. Careful evaluation of the best tumor thickness offers very useful prognostic guidance hiv infection rate ethiopia famvir 250 mg order without prescription. It also corresponds to the zone of transformation of the horizontally oriented reticular dermis elastic fibers to the vertically aligned ones of the papillary dermis. The Clark level refers to levels of invasion in accordance with depth of penetration of the dermis. Brisk lymphocytic responses tend to be a characteristic of skinny melanomas whereas absence of a lymphocytic response is generally seen in thick melanomas. Category A � Brisk: the lymphocytes infiltrate the tumor and prolong along the entire of the bottom of the lesion. Note the lymphocytic infiltrate, plasma cells, abundant melanin-containing macrophages, scarring, and conspicuous vasculature. It is found in thicker tumors and is associated with an increased risk of local recurrence, regional lymph node metastases, and diminished survival. More just lately, molecular strategies including reverse transcriptase polymerase chain response for tyrosinase messenger rNa have been proposed. Using these markers as a half of a panel taking a look at a number of traces of differentiation is also of sensible use, corresponding to inclusion of keratins to exclude epithelial tumors. In morphologically difficult instances, a panel of stains that helps the ultimate word analysis by their pattern of reactivity or nonreactivity is very useful. It ought to not often if ever be used as the only criterion by which a diagnosis of melanoma is achieved. S-100 protein stays the yardstick in the immunohistochemical diagnosis of melanoma. In cases where the analysis stays doubtful, use of a battery of the newer immunohistochemical markers could additionally be of nice worth. Staining of Langerhans cells can typically be a problem, particularly when assessing the extent of intraepidermal melanocyte unfold. S-100 protein can also be expressed in a number of breast carcinomas and undifferentiated carcinomas. More than 20 members of this family exist and monoclonal antibodies are available for a lot of of them. While not nicely established in large sequence, there could additionally be some selectivity of the isoforms between melanoma and different historically S-100 protein reactive neoplasms within the differential prognosis. Other possible indications include ulcerated tumors, tumors with 50% or extra regression, tumors having achieved the vertical progress section, and those lesions which have been biopsied and contain the deep margin. Similarly, highly 1238 Melanoma S-100 protein reactive, but the antibody additionally reacts with hepatocellular carcinoma and breast most cancers cells. While it lacks specificity and stains other cells it may be useful in desmoplastic melanoma. Diagnostic difficulties are unlikely to be encountered provided S-100 protein and/or other melanoma markers have been included within the antibody panel. In addition, distinguishing between balloon cell melanocytic lesions and xanthomatous infiltrates could require immunohistochemical affirmation, significantly if no residual recognizable melanocytic part is visible. In such circumstances, optimistic melanocytic markers are obviously of main diagnostic importance. Few of these are validated to the level needed for routine application to medical samples; virtually all are reported in retrospective cohorts. Use of a quantity of markers and utility of rigorous methods of quantification have efficacy, distinguishing different prognostic groups. Its role in predicting biological conduct is controversial; thus, though in earlier research increased expression in thick tumors was thought to correlate with poor survival, extra recently it has been claimed that elevated expression in thin tumors (< 1. Increased Ki-67 expression also correlates with overexpression of p53 protein and loss of p16 (see below). Cyclin D1 may be of help in differentiating between a banal nevus and a nevoid melanoma or a nevic part within a melanoma. Its expression all through the total thickness of a melanoma has been reported in as a lot as 60% of circumstances, whereas staining may be absent or restricted to solely occasional cells in the superficial facet of a nevus. Histological variants of melanoma Quite a spread of histological variants have been described. It was further postulated that such tumors appeared to have a greater prognosis than classic melanoma. Minimal deviation melanoma is characterized by the presence of an expansile nodule exhibiting solely gentle to moderate cytological atypia. It lacks the disorderly, extra marked pleomorphism of conventional epithelioid or spindled cell melanoma. Subtypes which could probably be included inside this class of minimal deviation are nevoid melanoma, small cell melanoma, and spitzoid melanoma. We prefer these categories for histologic classification and these three are handled under. Because nevoid melanoma is commonly misdiagnosed as a banal nevus, subsequent delay in appropriate remedy is frequent, with probably devastating consequences. Follow-up information indicates a recurrence rate of 50%, a metastasis fee of 25�50% and a mortality price of a minimum of 25%. In nodular tumors, the dermis is similarly skinny and stretched instantly over the surface of a dense domeshaped tumor cell population. Junctional activity in either variant is usually minimal and limited to atypical cells distributed predominantly along the basal layer of the epidermis. Verrucous variants have to be distinguished from keratotic melanocytic nevi, an important histological discriminants being the lack of maturation, delicate pleomorphism, and mitotic exercise. Banal nevi present solely very scattered constructive cells within the superficial part of the dermal component, whereas in melanoma they may be quite a few and present all through the thickness of the lesion. Dermal nevi are solely positive in the most superficial part of the nevus, whereas in melanoma positive cells could additionally be identified all through the depth of the tumor. Such tumors, which current on the scalp or developing in a congenital nevus, are extremely aggressive. We reserve the term for a high-grade melanoma, presenting as a small blue cell tumor harking back to type-B nevus cells. Spitzoid melanoma the diagnosis of Spitz nevus, and particularly its distinction from melanoma, is one of the most difficult areas in dermatopathology. More lately, Spatz and coworkers13 have devised a grading system for dividing atypical Spitz nevi into low, medium, and high-risk classes (of being frankly malignant). Cases in this class may not represent neoplasms with the full biological potential of normal melanoma; nonetheless, this class could additionally be tainted with Spitz nevi containing uncommon options.
Buy cheap famvir 250 mg on-line
The posterior basal segmental artery arises with the lateral basal segmental artery as a bifurcation of the descending branch of the left pulmonary artery and proceeds inferiorly and posteriorly to the posterior bronchopulmonary segment hiv infection during pregnancy famvir 250 mg buy cheap line. The lateral basal segmental artery proceeds inferiorly and laterally to supply the lateral bronchopulmonary segment antiviral research abbreviation purchase 250 mg famvir free shipping. The main pulmonary artery, proper pulmonary artery, and the left pulmonary artery run usually in the axial plane. Depending on the extent of the picture, one could possibly see all three of those vessels. Above and beneath the hilum the segmental branches are often oriented longitudinally. It runs upward, to the back and to the left, when it turns sharply to the left and caudally to the hilum of the left lung. It lies in entrance of the descending aorta, beneath the curve of the aortic arch, and is related to the arch by the ligamentum arteriosum. The left pulmonary artery is short and bifurcates in the left hilum into ascending and descending branches, which supply the left higher and lower lobes, respectively. More typically, the prognosis is made by finding filling defects within the segmental branches. When the segmental arteries are touring in a cephalad or caudal course, the filling defect is manifest as a low-density circle, often with a rim of distinction around the exterior where some blood is reaching the periphery. The sensitivity and specificity of the take a look at has now risen to a degree at which angiography is normally reserved for these instances where interventional therapy is being thought-about. Pulmonary Microcirculation the pulmonary circulation plays the function of a universal blood filter among the venous and arterial territories. Particles larger than 75 m are often retained at the stage of the pulmonary arterioles. The sizes of the capillaries are about eight to 9 m in diameter and 6 to 18 m in size. The measurement of the capillaries varies markedly in accordance with the gravity and position of the person. Experimentally it was established that particles as giant as 400 m might be recovered within the venous facet of the pulmonary circulation, indicating precapillary shunts between pulmonary arteries and veins. The peripheral pulmonary artery and alveolar capillary network are massive vascular beds of about 70 to 90 m2, in the adult, allowing intimal contact of the blood circulation with the oxygen from the air within the alveoli. The primary elements of this community, the capillary segments, are brief cylindric tubes joined at both ends by two adjacent segments, making a community of hexagonal facet. The pulmonary artery, regardless of high quantity and circulate, has no capability of lung vitamin. The blood supply to the bronchial connective tissue of the lung is a part of the systemic circulation. There is free communication between the capillaries of the pulmonary and bronchial systems, and these capillary beds might drain into both the systemic venous system by way of the azygos vein or via the pulmonary veins into the left atrium. The interrelation of the 2 circulations on the capillary stage supplies a potential shunt, which may serve to prevent elevation of capillary hydrostatic strain, ought to increase in both right or left atrial stress happen unilaterally. The bronchial vessels can provide collateral circulation to the lungs when the pulmonary arterial supply is interrupted. The bronchial arteries are significant in size as a lot as the terminal bronchiole, where the pulmonary artery circulation takes over the vitamin. The small arteriolar branches of the bronchial artery may, however, prolong to the alveolar ducts and sometimes even into the lung parenchyma across the alveolar sacs. The bronchial arteries vascularize the bronchial partitions, muscles, glands, and cartilage. The bronchial arteries provide the vasa vasorum to the partitions of the pulmonary arteries and the vasa nervorum to the nerves. The blood from the bronchial arteries drains into the systemic veins, bronchial veins, tributaries of the azygos vein, or superior vena cava. From the secondary or tertiary bronchi, the blood of the bronchial arteries drains into the alveolar capillary community at precapillary, capillary, and postcapillary websites, and subsequently into the pulmonary veins. Dense vascular networks around the bronchi are arteriolar networks terminating in bronchial capillaries and numerous bronchial venous plexuses with a attribute irregular form and course. There are connections of bronchial capillaries with the bronchial venous plexuses, and these vascular parts exist either within the bronchial wall or in the peribronchial connective tissue. These microvascular structures are observed along the whole size of the bronchial tree as far distally because the terminal bronchioles, but with decreased numbers in proportion to the discount of the caliber of the bronchi and bronchioles. The connective tissue across the pulmonary arteries incorporates an identical vascular community, but with much less numerous vessels. Most of the blood of juxtapleural bronchial artery drains into the pulmonary capillary community. A fantastic vascular network exists in the mediastinal pleura, and the bronchial venous plexus within the pleura communicates with branches of the pulmonary vein. There are precapillary and postcapillary anastomoses between the bronchial artery circulation and the pulmonary arterial circulation. There are communications of bronchial venous plexuses with small branches of the pulmonary vein. Bronchial vessels across the pulmonary vein additionally talk with small branches of the pulmonary vein. Therefore, all bronchial venous techniques across the airway and blood vessels are connected with the pulmonary vein through small branches. There are direct communications of bronchial venous plexuses with the encompassing alveolar capillaries by way of small venules, and likewise noticed in both bronchi and bronchioles. A, Anterior view of an injection solid of the pulmonary arteries, pulmonary veins, left ventricle, and aortic arch. Note location of pulmonary veins draining into the left atrium at a degree inferior to the pulmonary arteries. A, Anterior view of an injection cast of the pulmonary arteries, pulmonary veins, and tracheobronchial tree. D, Right oblique view of the late phase of the angiography exhibiting the pulmonary veins. A, Early phase of the anterior view of an angiogram of the right pulmonary artery. A, Anterior view of an injection forged of the left pulmonary artery and pulmonary veins. A, Anterior view of the early part of the angiogram of the left pulmonary artery. B, Late section of the left angiography exhibiting the lateral view of the pulmonary veins. A, Axial picture demonstrating bifurcation of primary pulmonary artery into the best and left pulmonary arteries. C, Slightly cranial axial picture exhibiting the left pulmonary artery passing up and over the left mainstem bronchus. A and B, Image on the stage of bifurcation of the main pulmonary artery demonstrating a saddle embolus extending into the best and left pulmonary arteries. Axial image at a extra caudal degree showing emboli (filling defects) in the segmental pulmonary arteries.
Famvir 250 mg line
Due to fibrous replacement of the subcutaneous fat hiv infection rates by continent famvir 250 mg buy low price, the eccrine glands seem to be situated abnormally excessive throughout the dermis quite than at the dermosubcuticular interface hiv infection rates heterosexual vs homosexual buy 250 mg famvir mastercard. In the linear and generalized variants in particular, the inflammatory adjustments may have an effect on the underlying skeletal muscle. In the late stages, dermal sclerosis is still evident, however the dermis appears thinned due to concomitant atrophy. Calcinosis cutis is often seen and neuritis much like that seen in indeterminate leprosy has additionally been documented. Vascular adjustments, together with thromboses, purpura, and hemosiderosis, nonetheless, are conspicuous within the former, whereas bizarre fibroblasts, elastosis, and endarteritis obliterans are characteristic of the latter. Atrophoderma of Pasini and Pierini Clinical options atrophoderma is a uncommon, major dermal atrophic strategy of unsure nature. Eosinophilic fasciitis the medical features of painful, tender swelling, stiffness, and sclerodermiform induration have an effect on (in decreasing order of frequency) the forearms, upper arms and lower legs, thighs, hands, trunk, neck, and toes. Inflammatory arthritis (predominantly involving the palms, wrists, and knees) and carpal tunnel syndrome occur in about 25% of sufferers. Pathogenesis and histological options It is still controversial whether this disease represents a variant of morphea. Within the superficial dermis is a perivascular and interstitial continual inflammatory cell infiltrate consisting of lymphocytes and histiocytes. In early lesions the collagen bundles are homogenized and swollen but, with development, sclerosis usually supervenes within the deeper reticular dermis. Pathogenesis and histological options the etiology and pathogenesis of eosinophilic fasciitis are unknown. Lymphoid follicles, sometimes with germinal facilities, are also occasionally evident. Sclerodermoid and eosinophilic fasciitis-like syndromes have been described as options of the toxic oil and L-tryptophan-related eosinophilia� myalgia syndromes. In some sufferers probably the most conspicuous adjustments have included fibrosis involving the papillary dermis, periappendageal connective tissue sheath and subcutaneous fat. Polymyositis/dermatomyositis Clinical options polymyositis is a rare inflammatory disorder of muscle, the etiology of which is unknown. Overlap syndromes happen extra regularly in polymyositis than in dermatomyositis and present a marked female predominance (9:1). Muscle atrophy develops later in the course of the illness when fibrosis and troublesome contractures could supervene. Juvenile dermatomyositis has additionally been associated with ischemic ulcerative colitis and celiac disease. In addition to anti-Jo-1 antibody, further newly described antibodies embrace pM-1, Ku, Mi-1, -2 and -3, and pa-1. In a current research analyzing patients with dermatomyositis in China, nasopharyngeal most cancers was the most frequent affiliation, adopted by lung most cancers. Spread to the thoracic muscle tissue can end result in extreme respiratory difficulties; terminal bronchopneumonia is therefore an essential explanation for demise. Digital ulcers, periungual infarcts, and oral ulcers are related manifestations. There is basal cell hydropic degeneration and cytoid bodies are current within the superficial dermis. In some cases the presence of marked hyperkeratosis, follicular plugging, dermal edema, and increased quantities of basement membrane-like material leads to appreciable histological overlap with lupus erythematosus, and clinicopathological correlation is crucial. In addition, their sera invariably contained excessive titers of antibody to a saline extractable nuclear antigen (eNa), U1-rNp, and speckled antinuclear antibody. In the sunshine of information from subsequent experience, the above, somewhat simplistic, overview has needed to be modified. Muscle necrosis in dermatomyositis tends to involve small teams of fibers, whereas in polymyositis the affected fibers are inclined to be single and sparse. Denervation neuropathic features are additionally sometimes current, presumably as a outcome of involvement by the inflammatory process of small intramuscular nerve fibers. In childhood dermatomyositis, vascular modifications affecting the capillaries, venules, and arterioles are frequent. Biopsies from cutaneous lesions with no typical options could show histological options just like those of subacute lupus. Livedoid vasculitis with ulcers has also been documented and was related to poor prognosis in the single patient described. One group of authors suggested that matrilin-1, a cartilage matrix protein, is the goal of autoreactivity. Differential diagnosis Chondrodermatitis nodularis helicis differs by the presence of attribute layering of fibrin, granulation tissue, and cartilage with degenerative adjustments. Psoriasiform hyperplasia with fused club-shaped rete ridges and an higher dermal perivascular inflammatory cell infiltrate. It is characterised by diffuse dryness of the pores and skin with hyperpigmented scales and focal crusting. CaD is characterised by subacute dermatitis with variable psoriasiform dermatitis and an atypical lymphocytic infiltrate. A dense interstitial and perivascular continual inflammatory cell infiltrate is present in the higher dermis. Follicular disruption and publicity of the sebaceous antigen are implicated in the stimulation of an inflammatory process involving lymphocytes, cytokines, and eosinophils. Clinical features erythema elevatum diutinum (eeD), a rare persistent illness of unknown etiology, is a part of the spectrum of cutaneous leukocytoclastic vasculitis. Stains to exclude infective causes for the fibrovascular and mobile alterations may be required. Direct immunofluorescence in the latter situation reveals Iga deposits around keratinocytes. Kawasaki disease is identified by a history of fever of 5 days length, plus 4 of the following 5 options: � bilateral nonpurulent conjunctivitis, � adjustments of the oropharynx, together with an injected pharynx, injected and/ or dry fissured lips, and/or strawberry tongue, � modifications of the peripheral extremities, including edema and/or erythema of the palms and the ft (usually adopted by desquamation), � a nonvesicular, polymorphous, erythematous exanthema, � cervical lymphadenopathy with lymph nodes measuring 1. Conditions embody bullous pemphigoid, epidermolysis bullosa acquisita, pemphigus herpetiformis, pemphigus vegetans, mucocutaneous pemphigus vulgaris, pemphigus foliaceus, antiepiligrin cicatrical pemphigoid, Iga dermatosis, dermatitis herpetiformis, intraepidermal neutrophilic Iga dermatosis, and endemic pemphigus foliaceus. Type 2 infections sort 2 infections are in depth infections which are focal or trivial within the immunocompetent. Type 4 infections sort four infections are metastatic from systemic disease and embrace Pseudomonas, Histoplasma, Coccidioides, Blastomyces, Nocardia, Aspergillus, Cryptococcus, Candida, and Mucor. Occasional features include a diffuse dermal infiltrate, wedgeshaped hypergranulosis, and a microscopic subepidermal blister. Bullous lesions are characteristically cell-poor, with inflexible papillary dermal capillary walls thickened by eosinophilic, paS-positive material. Differential prognosis the histological differential diagnoses embrace folliculitis (suppurative or eosinophilic), scabies, secondary syphilis, and a drug eruption. Occasionally, elaborated Demodex folliculorum mites are noticed in the perifollicular dermis when intradermal rupture of an involved, distended follicle has occurred. Differential diagnosis the main histological differential diagnoses are eosinophilic pustular folliculitis (Ofuji disease) and ppe. Serial sectioning may be required to determine foci of leukocytoclastic vasculitis.
Real Experiences: Customer Reviews on Famvir
Owen, 58 years: With progression, filamentous transformation comes to affect the complete cell, and nuclear, cytoplasmic, and desmosomal remnants may be identified throughout the filamentous mass. Lichen sclerosus is an additional incessantly found associated condition and may be pathogenetically related to verrucous carcinoma. This artery passes around the splenium, operating anteriorly within the supracallosal cistern and anastomosing with the distal branches of the anterior pericallosal artery.
Trompok, 34 years: In psoriasis the acanthosis is often extra marked and often strikingly common, the rete ridges are skinny and often fused, the suprapapillary plate is thinned, parakeratosis is usually confluent, and characteristic collections of neutrophils are seen within the overlying parakeratotic stratum corneum in affiliation with spongiform degeneration of the underlying superficial epidermis. Histological features Unlike typical conjunctival nevus, which may function spindled cells oriented parallel to the epithelial floor, Spitz nevus options fascicles of spindled nevus cells that are normally oriented perpendicular to the epithelial floor and are uniformly and symmetrically organized. Lichen planus is characterised by large numbers of lesions in contradistinction to the only papule or plaque of lichenoid.
Vasco, 46 years: It is now appreciated that histologically the 2 conditions are indistinguishable. Condylomatous (warty) carcinoma Clinical features Condylomatous carcinoma is a slowly rising, verruciform low- to intermediate-grade hpV-related tumor, grossly just like large condyloma however with malignant histology and potential for nodal metastasis. Low-titer rheumatoid issue and antinuclear antibody are sometimes features and, in occasional patients, a cryoglobulin is recognized.
8 of 10 - Review by K. Ramon
Votes: 193 votes
Total customer reviews: 193