Flutamide dosages: 250 mg
Flutamide packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills
250 mg flutamide discount amex
An H&E�stained specimen showing a longitudinal layer of smooth muscle cells from the wall of the gut symptoms 8 dpo 250 mg flutamide discount otc. More intensely stained tissue at the prime and bottom of this photomicrograph represents connective tissue symptoms youre pregnant flutamide 250 mg order on-line. The three germ layers embrace the ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm, which give rise to all the tissues and organs. The derivatives of the ectoderm may be divided into two main lessons: floor ectoderm and neuroectoderm. Surface ectoderm offers rise to: � � � � � � � epidermis and its derivatives (hair, nails, sweat glands, sebaceous glands, and the parenchyma and ducts of the mammary glands), cornea and lens epithelia of the eye, enamel organ and enamel of the teeth, components of the inner ear, adenohypophysis (anterior lobe of pituitary gland), and mucosa of the oral cavity and decrease part of the anal canal. Nerve tissue consists of an enormous quantity of thread-like myelinated axons held together by connective tissue. The axons have been cross-sectioned and seem as small, purple, dot-like constructions. The clear house surrounding the axons beforehand contained myelin that was dissolved and lost throughout preparation of the specimen. It types a delicate community around the myelinated axons and ensheathes the bundle, thus forming a structural unit, the nerve. An Azan-stained section of a nerve ganglion, displaying the massive, spherical nerve cell bodies and the nuclei of the small satellite tv for pc cells that encompass the nerve cell bodies. It offers rise to: � connective tissue, including embryonic connective � � � � � � tissue (mesenchyme), connective tissue correct (loose and dense connective tissue), and specialized connective tissues (cartilage, bone, adipose tissue, blood and hemopoietic tissue, and lymphatic tissue); striated muscle tissue and easy muscular tissues; coronary heart, blood vessels, and lymphatic vessels, including their endothelial lining; spleen; kidneys and the gonads (ovaries and testes) with genital ducts and their derivatives (ureters, uterine tubes, uterus, ductus deferens); mesothelium, the epithelium lining the pericardial, pleural, and peritoneal cavities; and the adrenal cortex. Thyroid and parathyroid glands develop as epithelial outgrowths from the floor and partitions of the pharynx; they then lose their attachments from these sites of authentic outgrowth. As an epithelial outgrowth of the pharyngeal wall, the thymus grows into the mediastinum and likewise loses its unique connection. In the early embryo, it types the wall of the primitive gut and offers rise to epithelial portions or linings of the organs arising from the primitive intestine tube. Derivatives of the endoderm embrace: � alimentary canal epithelium (excluding the epithe- lium of the oral cavity and lower part of the anal canal, that are of ectodermal origin); Keeping these few primary information and concepts about the basic 4 tissues in mind can facilitate the task of analyzing and decoding histologic slide material. The first goal is to recognize aggregates of cells as tissues and decide the special traits that they current. Are they involved with their neighbors, or are they separated by definable intervening materials The construction and the perform of every basic tissue are examined in subsequent chapters. However, this separation is important to perceive and respect the histology of the assorted organs of the physique and the means by which they operate as useful items and integrated techniques. Schematic drawing illustrates the derivatives of the three germ layers: ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm. Most of the tumors derive from the cells that originate from a single germ cell layer. However, if the tumor cells come up from the pluripotential stem cells, their mass could comprise cells that differentiate and resemble cells originating from all three germ layers. Since pluripotential stem cells are primarily encountered in gonads, teratomas almost all the time occur within the gonads. In the ovary, these tumors usually develop into stable lots that comprise characteristics of the mature fundamental tissues. Although the tissues fail to kind functional structures, frequently organ-like constructions could additionally be seen. Moreover, ovarian teratomas are often benign, whereas teratomas within the testis are composed of much less differentiated tissues that often lead to malignancy. However, with higher magnification, as shown in the insets (a�f), mature differentiated tissues are evident. Mature teratomas are frequent ovarian tumors in childhood and in early reproductive age. Again, the essential level is the ability to acknowledge aggregates of cells and to determine the particular traits that they exhibit. In the middle is an H&E�stained section of an ovarian teratoma seen at low magnification. This mass consists of assorted basic tissues which would possibly be nicely differentiated and easy to establish at greater magnification. The abnormal function is the dearth of organization of the tissues to form practical organs. The tissues within the boxed areas are seen at greater magnification in micrographs a�f. The greater magnification permits identification of a few of the basic tissues which are present inside this tumor. All organs are made up of only four primary tissue types: epithelium (epithelial tissue), connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nerve tissue. Epithelium is classified primarily based on morphologic characteristics: number of cell layers and form of cells. A typical neuron is made up of a cell body, a single lengthy axon to carry impulses away from the cell body, and multiple dendrites to obtain impulses and carry them toward the cell physique. It under- lies and supports (structurally and functionally) the other three basic tissues. Connective tissue is classified into three categories based mostly on the content material of its extracellular matrix and the characteristics of individual cells: embryonic, proper connective tissue (loose and dense), and specialized connective tissues. Ectodermal-derived constructions develop either from floor ectoderm or neuroectoderm. All forms of muscle cells include the contractile proteins actin and myosin, which are arranged in myofilaments and are responsible for muscle contraction. Skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle cells have cross-striations that are fashioned by a specific association of myofilaments. Neuroectoderm provides rise to the neural tube, the neural crest, and each their derivatives. Mesoderm offers rise to connective tissue; muscle tissue; heart, blood, and lymphatic vessels; spleen; kidneys and gonads with genital ducts and their derivatives; mesothelium, which traces body cavities; and the adrenal cortex. Endoderm provides rise to alimentary canal epithelium; extramural digestive gland epithelium (liver, pancreas, and gallbladder); epithelium of the urinary bladder and most of the urethra; respiratory system epithelium; thyroid, parathyroid, and thymus gland; parenchyma of the tonsils; and epithelium of the tympanic cavity and auditory (Eustachian) tubes. Epithelium also varieties the secretory portion (parenchyma) of glands and their ducts. In addition, specialised epithelial cells operate as receptors for the particular senses (smell, style, listening to, and vision). The cells that make up epithelium have three principal characteristics: � They exhibit useful and morphologic polarity. In other words, completely different functions are related to three distinct morphologic floor domains: a free floor or apical area, a lateral domain, and a basal domain. The properties of every domain are determined by particular lipids and integral membrane proteins.
Diseases
- Brachydactyly type A5 nail dysplasia
- Arthrogryposis ophthalmoplegia retinopathy
- Phenylketonuria
- Cogan Reese syndrome
- Trichomoniasis
- M?llerian derivatives, persistent
Order 250 mg flutamide with mastercard
The neonatal line within the enamel and dentin of the human deciduous enamel and first everlasting molar medications safe in pregnancy flutamide 250 mg generic amex. During amelogenesis treatment toenail fungus order flutamide 250 mg line, enamel formation is influenced by the path of the ameloblasts. Note the numerous matrix-containing secretory vesicles within the cytoplasm of the processes. Digestive System I cyclical alterations of their morphology that correspond to cyclical entry of calcium into the enamel. The histologic feature that marks the cycles of maturationstage ameloblasts is a striated or ruffled border. A cluster of mitochondria and an accumulation of actin filaments within the proximal terminal web within the base of the cell account for the eosinophilic staining of this area in hematoxylin and eosin (H&E)� stained paraffin sections. They maintain the integrity and orientation of the ameloblasts as they transfer away from the dentoenamel junction. Actin filaments joined to these junctional complexes are involved in shifting the secretory-stage ameloblast over the developing enamel. Thus, in mature enamel, the course of the enamel rod is a report of the trail taken earlier by the secretory-stage ameloblast. At their base, the secretory-stage ameloblasts are adjacent to a layer of enamel organ cells referred to as the stratum intermedium. The plasma membrane of those cells, especially at the base of the ameloblasts, contains alkaline phosphatase, an enzyme active in calcification. Stellate enamel organ cells are exterior to the stratum intermedium and are separated from the adjacent blood vessels by a basal lamina. This photomicrograph of an H&E�stained section of a growing human tooth shows ameloblasts and odontoblasts as they start to produce enamel (E) and dentin (D), respectively. The enamel seems deep purple in this image and is adjoining to the reddish purple layer of mature dentin (D). The distinct pink strains are associated to the accumulation of actin filaments in ameloblasts. A layer of stratum intermedium is now not current throughout this stage of ameloblast maturation. During slide preparation, apical surfaces of ameloblasts have been indifferent from the enamel. Cells from underlying stratum intermedium, stellate reticulum, and outer dental epithelium collapse on one another and undergo reorganization, making it impossible to distinguish them as individual layers. Finally, the blood vessels invaginate into this newly reorganized layer to form the papillary layer containing stellate papillary cells that are adjacent to the maturation-stage ameloblasts. The maturation-stage ameloblasts and the adjoining papillary cells are characterised by quite a few mitochondria. Their presence signifies mobile activity that requires giant amounts of vitality and displays the operate of maturation-stage ameloblasts and adjoining papillary cells as a transporting epithelium. Recent advances within the molecular biology of ameloblast gene products have revealed the enamel matrix to be highly heterogeneous. Listed here are the principal proteins within the extracellular matrix of the developing enamel: � enamel matures. Low-molecular-weight merchandise of this cleavage are retained in the mature enamel, usually localized on the floor of enamel crystals. Tuftelins, the earliest detected proteins positioned close to the dentinoenamel junction. The maturation of the growing enamel results in its continued mineralization in order that it turns into the hardest substance in the body. The ameloblasts degenerate after the enamel is fully fashioned, at about the time of tooth eruption through the gum. Ameloblastins, signaling proteins produced by ameloblasts from the early secretory to late maturation stages. Ameloblastins are believed to guide the enamel mineralization course of by controlling elongation of the enamel crystals and to type junctional complexes between particular person enamel crystals. These proteins bear proteolytic cleavage because the the basis is the part of the tooth that fits into the alveolus or jaw socket within the maxilla or mandible. Cementum is a skinny layer of bone-like material that covers roots of teeth beginning on the cervical portion of the tooth on the cementoenamel junction and continuing to the apex. Cementum is produced by cementoblasts (large cuboidal cells that resemble the osteoblasts of the floor of growing bone). Cementoblasts secrete an extracellular matrix referred to as cementoid that additional undergoes mineralization. A layer of cementoblasts is present on the outer surface of the cementum, adjacent to the periodontal ligament. During cementogenesis, cementoblasts are included into the cementum and become cementocytes, cells that carefully resemble osteocytes in bone. The lacunae and canaliculi in the cementum comprise the cementocytes and their processes, respectively. They resemble these constructions in bone that comprise osteocytes and osteocyte processes. Collagen fibers that project out of the matrix of the cementum and embed within the bony matrix of the socket wall type the majority of the periodontal ligament. This mode of attachment of the tooth in its socket allows slight motion of the tooth to occur naturally. It also types the basis of orthodontic procedures used to straighten much less hydroxyapatite than enamel, about 70%, but greater than is found in bone and cementum. The apical surface of the odontoblast is in touch with the forming dentin; junctional complexes between the odontoblasts at that level separate the dentinal compartment from the pulp chamber. The layer of odontoblasts retreats because the dentin is laid down, leaving odontoblast processes embedded in the dentin in slender channels called dentinal tubules. The tubules and processes continue to elongate because the dentin continues to thicken by rhythmic development. The rhythmic development of dentin produces sure "growth lines" in the dentin (incremental traces of von Ebner and thicker traces of Owen) that mark vital developmental occasions corresponding to birth (neonatal line) and when uncommon substances corresponding to lead are incorporated into the growing tooth. This photomicrograph of a decalcified tooth exhibits the centrally situated dental pulp, surrounded by dentin on both sides. The dental pulp is a gentle tissue core of the tooth that resembles embryonic connective tissue, even in the adult. Dentin contains the cytoplasmic processes of the odontoblasts inside dentinal tubules. The cell bodies of the odontoblasts are adjoining to the unmineralized dentin called the predentin. The darkish outline of the dentinal tubules, as seen in each insets, represents the peritubular dentin, which is the extra mineralized a half of the dentin. Predentin is the newly secreted natural matrix, closest to the cell body of the odontoblast, which has but to be mineralized. Digestive System I An uncommon characteristic of the secretion of collagen and hydroxyapatite by odontoblasts is the presence, in Golgi vesicles, of arrays of a formed filamentous collagen precursor. Granules believed to comprise calcium connect to these precursors, giving rise to structures called abacus bodies.
Buy cheap flutamide 250 mg on line
Osteoporosis is a illness that affects an estimated 75 million people in the United States treatment 100 blocked carotid artery cheap 250 mg flutamide with mastercard, Europe medicine 93 cheap flutamide 250 mg overnight delivery, and Japan, together with one-third of postmenopausal women and most of the aged inhabitants. This picture shows a piece from the trabecular bone obtained from a vertebral physique of a healthy individual. This specimen was obtained from a vertebral physique of an elderly woman displaying intensive signs of osteoporosis. Compare the sample of trabecular structure in osteoporosis with normal vertebral bone. Femoral head and neck fractures (commonly often identified as hip fractures), wrist fractures, and compressed vertebrae fractures are widespread injuries that regularly disable and confine an elderly person to a wheelchair. Individuals suffering from fractures are at higher risk for death, not directly from the fracture, however from the problems of hospitalization due to immobilization and increased threat of pneumonia, pulmonary thrombosis, and embolism. Traditional treatment of individuals with osteoporosis contains an improved food plan with vitamin D and calcium supplementation and average train to assist gradual additional bone loss. In addition to diet and train, pharmacologic remedy directed toward slowing down bone resorption is employed. Until just lately, the therapy of selection in postmenopausal girls with osteoporosis was hormone alternative therapy with estrogen and progesterone. This group of pharmacologic brokers binds to estrogen receptors and acts as an estrogen agonist (mimicking estrogen action) in bone; in different tissues, it blocks the estrogen receptor motion (acting as an estrogen antagonist). Hormonal remedy in osteoporosis contains the usage of human parathyroid hormone recombinant. In intermittent doses, it promotes bone formation by increasing osteoblastic exercise and bettering thickness of trabecular bone. Osteocalcin, which is produced by osteoblasts, is linked to a model new pathway regulating vitality and glucose metabolism. Rickets may be brought on by inadequate quantities of dietary calcium or insufficient vitamin D (a steroid prohormone), which is needed for absorption of calcium by the intestines. An X-ray of a kid with advanced rickets presents traditional radiological symptoms: bowed decrease limbs (outward curve of long bones of the leg and thighs) and a deformed chest and cranium (often having a particular "square" appearance). In addition to its affect on intestinal absorption of calcium, vitamin D can additionally be needed for regular calcification. Vitamin A deficiency suppresses endochondral growth of bone; vitamin A extra leads to fragility and subsequent fractures of long bones. Vitamin C is essential for synthesis of collagen, and its deficiency results in scurvy. Another type of insufficient bone mineralization often seen in postmenopausal girls is the situation generally identified as osteoporosis (see Folder eight. Understanding the endocrine position of bone tissue will improve diagnosis and management of sufferers with osteoporosis, diabetes mellitus, and other metabolic issues. Indirect (secondary) bone healing involves responses from periosteum and surrounding gentle tissues as well as endochondral and intramembranous bone formation. This sort of bone repair happens in fractures that are treated with nonrigid or semirigid bone fixation. Repair of bone fracture can happen in two processes: direct or indirect bone therapeutic. Direct (primary) bone healing occurs when the fractured bone is surgically stabilized with compression plates, thereby proscribing movement utterly between fractured fragments of bone. In this process, bone undergoes internal transforming similar to that of mature bone. The chopping cones shaped by the osteoclasts cross the fracture line and generate longitudinal resorption canals which are later crammed by bone-producing osteoblasts residing in the closing cones (see page 235 for details). This course of results in the preliminary response to bone fracture is similar to the response to any injury that produces tissue destruction and hemorrhage. Injury to the accompanied soft tissues and degranulation of platelets from the blood clot are responsible for secreting cytokines. Absence or extreme hyposecretion of thyroid hormone throughout development and infancy results in failure of bone development and dwarfism, a situation generally recognized as congenital hypothyroidism. Instead, irregular thickening and selective overgrowth of palms, toes, mandible, nostril, and intramembranous bones of the skull happens. This condition, often identified as acromegaly, is attributable to elevated activity of osteoblasts on bone surfaces. This hormone stimulates growth generally and, particularly, growth of epiphyseal cartilage and bone. It acts instantly on osteoprogenitor cells, stimulating them to divide and differentiate. The initial response to the damage produces a fracture hematoma that surrounds the ends of the fractured bone. The acute inflammatory response develops and is manifested by infiltration of neutrophils and macrophages, activation of fibroblasts, and proliferation of capillaries. Newly shaped fibrocartilage fills the hole at the fracture site producing a delicate callus. The osteoprogenitor cells from the periosteum differentiate into osteoblasts and start to deposit new bone on the outer floor of the callus (intramembranous process) till new bone forms a bony sheath over the fibrocartilaginous soft callus. The cartilage within the soft callus calcifies and is gradually changed by bone as in endochondral ossification. Bone remodeling of the exhausting callus transforms woven bone into the lamellar mature structure with a central bone marrow cavity. Hard callus is progressively changed by the action of osteoclasts and osteoblasts that restores bone to its original shape. This process is reflected by infiltration of neutrophils adopted by the migration of macrophages. Fibroblasts and capillaries subsequently proliferate and develop into the positioning of the damage. Also, particular mesenchymal stem cells arrive to the positioning of damage from the encompassing gentle tissues and bone marrow. Both fibroblasts and periosteal cells take part during this part of the therapeutic. Granulation tissue transforms into fibrocartilaginous gentle callus, which gives the fracture a steady, semirigid structure. The dense connective tissue and newly shaped cartilage grows and covers the bone at the fractured web site, producing a soft callus. This callus will form no matter the fractured parts being in quick apposition to each other, and it helps stabilize and bind collectively the fractured bone. Bony callus replaces fibrocartilage on the fracture website and permits for weight bearing.
Discount flutamide 250 mg with mastercard
Hairs are snared within an outstretched strand o twisted cotton thread and pulled out medicine runny nose flutamide 250 mg generic on-line. Although waxing and plucking allow e ective temporary hair elimination symptoms 0f brain tumor cheap flutamide 250 mg with visa, everlasting epilation may be achieved with thermal destruction o the hair ollicle. It requires repetitive therapies over several weeks to months, can be ache ul, and can result in scarring. Alternatively, laser remedy directs speci c laser wavelengths to also permanently destroy ollicles. During this process, termed selective photothermolysis, only goal tissues absorb laser light and are heated. Surrounding tissues ail to absorb the selective wavelength and receive minimal thermal harm. For this purpose, light-skinned ladies with darkish hairs are better candidates or laser therapy because of the selective wavelength absorption by their hair. Advantageously, laser therapy can cowl a wider sur ace area than electrolysis and there ore requires ewer therapies. This enzyme is important or hair ollicle cell division and unction, and its inhibition leads to slower hair progress. E ornithine hydrochloride (Vaniqa) might require 4 to 8 weeks o use be ore changes are seen. Androgen-receptor Antagonists Antiandrogens are competitive inhibitors o androgen binding to the androgen receptor (Brown, 2009; Moghetti, 2000; Venturoli, 1999). Although these brokers e ectively deal with hirsutism, they carry a danger or several facet e ects. In addition, as antiandrogens, these medicine bear a theoretical threat o inter ering with external genitalia growth in male etuses o women using such medications in early being pregnant. Accordingly, these medicine are commonly used along side oral contraceptive pills, which immediate regular menses and provide e ective contraception. Spironolactone (Aldactone), in a dosage o 50 to a hundred mg orally twice every day, is the primary antiandrogen used currently within the United States. In addition to its antiandrogen e ects, this drug additionally a ects hair conversion rom vellus to terminal by its direct inhibition o 5 -reductase. O less prescribed alternate options, in Europe, Canada, and Mexico, the antiandrogen cyproterone acetate is used in an oral contraceptive pill. Flutamide is one other nonsteroidal antiandrogen marketed or the treatment o prostate cancer. Acne One half o pimples remedy is just like that or hirsutism and involves decreasing o androgen levels. In basic, mild nonin ammatory comedonal acne may be treated with topical retinoid monotherapy. I mild in ammatory pustules are present, topical retinoids are mixed with topical antimicrobial remedy or benzoyl peroxide. Moderate to extreme acne may require triple therapy with the above brokers or use o oral retinoids or oral antibiotics. For this cause, ladies with moderate to severe acne might bene t rom consultation with a dermatologist. Topical retinoids regulate the ollicular keratinocyte and normalize its desquamation. In addition, these agents also have direct antiin ammatory properties and thereby goal two actors linked to acne vulgaris (Zaenglein, 2006). Adapalene and tazarotene are additionally e ective (Gold, 2006; Leyden, Hair Removal Hirsutism is o ten treated by mechanical means, and these embody both depilation and epilation techniques. In addition to hair elimination, lightening hair shade with bleach is a cosmetic choice. Initially, a pea-sized dab suf cient to cowl the complete ace is applied every third evening and progressively elevated as tolerated to nightly application (Krowchuk, 2005). Topical benzoyl peroxide is bactericidal to P acnes by producing reactive oxygen species inside the ollicle. Topical antibiotics typically embrace erythromycin and clindamycin, whereas oral antibiotics most o ten used or pimples include doxycycline, minocycline, and erythromycin. Oral antibiotics are extra e ective than topical therapies but can have numerous aspect e ects corresponding to sun sensitivity and gastrointestinal upset. Despite its ef cacy, oral isotretinoin is teratogenic i taken through the rst trimester o being pregnant. Mal ormations sometimes contain the skull, ace, coronary heart, central nervous system, and thymus. There ore, isotretinoin administration is proscribed to women utilizing a extremely e ective methodology o contraception. American College o Obstetricians and Gynecologists: Diagnosis o abnormal uterine bleeding in reproductive-aged ladies. J Clin Endocrinol Metab eighty five:2434, 2000 Azziz R: the analysis and administration o hirsutism. Obstet Gynecol one hundred and one: 995, 2003 Azziz R, Carmina E, Dewailly D, et al: Position statement: criteria or de ning polycystic ovary syndrome as a predominantly hyperandrogenic syndrome: an Androgen Excess Society guideline. Am J Clin Dermatol 2:197, 2001 Banaszewska B, Duleba A, Spaczynski R: Lipids in polycystic ovary syndrome: position o hyperinsulinemia and e ects o met ormin. Hum Reprod Update 12:673, 2006 Brown J, Farquhar C, Lee O, et al: Spironolactone versus placebo or together with steroids or hirsutism and/or acne. J Invest Dermatol 98(Suppl):82S, 1992 Cui Y, Shi Y, Cui L, et al: Age-speci c serum antim�llerian hormone levels in ladies with and without polycystic ovary syndrome. Fertil Steril 102(1):230, 2014 Culiner A, Shippel S: Virilism and theca-cell hyperplasia o the ovary: a syndrome. Speci cally, a ew studies have proven an enchancment in acanthosis nigricans with insulin sensitizers (Walling, 2003). Other methods, including topical antibiotics, topical and systemic retinoids, keratolytics, and topical corticosteroids, have been tried with limited success (Schwartz, 1994). Rarely, oophorectomy is a viable possibility or ladies not in search of ertility who exhibit signs and signs o ovarian hyperthecosis and accompanying extreme hyperandrogenism. Hum Reprod Update 20(3):370, 2014 Diamanti-Kandarakis E, Kouli C, sianateli, et al: T erapeutic e ects o met ormin on insulin resistance and hyperandrogenism in polycystic ovary syndrome. N Engl J Med 361(12):1152, 2009 Dokras A, Bochner M, Hollinrake E: Screening women with polycystic ovary syndrome or metabolic syndrome. Obstet Gynecol 106:131, 2005 Dokras A, Cli ton S, Futterweit W, et al: Increased prevalence o nervousness signs in girls with polycystic ovary syndrome: systematic evaluation and meta-analysis. Fertil Steril 97(1):225, 2012 Dokras A, Cli ton S, Futterweit W, et al: Increased danger or irregular melancholy scores in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Semin Reprod Med 32:159, 2014 Dunai A: Insulin resistance and the polycystic ovary syndrome: mechanisms and implication or pathogenesis. Endocrine Rev 18:774, 1997 Dunai A, Finegood D: Beta-cell dys unction impartial o obesity and glucose intolerance in the polycystic ovary syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 81:942, 1996a Dunai A, Scott D, Finegood D, et al: the insulin-sensitizing agent troglitazone improves metabolic and reproductive abnormalities in the polycystic ovary syndrome.
Curbana (Canella). Flutamide.
- Colds, poor circulation, and other conditions.
- How does Canella work?
- Are there safety concerns?
- Dosing considerations for Canella.
- What is Canella?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96203
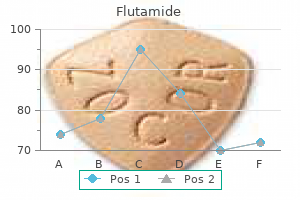
Purchase flutamide 250 mg amex
Serous glands have well-developed intercalated ducts and striated ducts that modify the serous secretion by each absorption of specific parts from the secretion and secretion of further elements to kind the final product treatment abbreviation safe flutamide 250 mg. Intercalated ducts are lined by low cuboidal epithelial cells that often lack any distinctive feature to suggest a perform other than that of a conduit medicine app order 250 mg flutamide with mastercard. Low-magnification electron micrograph of the sublingual gland, prepared by the fast freezing and freeze-substitution methodology, reveals the arrangement of the cells within a single acinus. Electron micrograph of the sublingual gland prepared by conventional fixation in formaldehyde. Note the appreciable enlargement and coalescence of the mucinogen granules and the formation of a serous demilune. This electron micrograph shows the basal portion of two secretory cells from a submandibular gland. Note the placement of the myoepithelial cell course of on the epithelial facet of the basal lamina. The cytoplasm of the myoepithelial cell contains contractile filaments and densities (arrows) similar to those seen in easy muscle cells. In mucus-secreting salivary glands, the intercalated ducts, when current, are brief and difficult to determine. Striated ducts are lined by a simple cuboidal epithe- Large quantities of adipose tissue usually happen within the parotid gland; that is considered one of its distinguishing options (Plate 52, page 564). Digestive System I lium that steadily turns into columnar as it approaches the excretory duct. The infoldings of the basal plasma membrane are seen in histologic sections as "striations. Basal infoldings related to elongated mitochondria are a morphologic specialization related to reabsorption of fluid and electrolytes. The striated duct cells even have numerous basolateral folds that are interdigitated with these of adjacent cells. The nucleus usually occupies a central (rather than basal) location in the cell. Striated ducts are the sites of: Submandibular Gland the submandibular glands are blended glands which would possibly be largely serous in humans. The giant, paired, blended submandibular glands are positioned underneath both side of the floor of the mouth, close to the mandible. A duct from each of the two glands runs ahead and medially to a papilla positioned on the ground of the mouth just lateral to the frenulum of the tongue. Some mucous acini capped by serous demilunes are generally discovered among the predominant serous acini. For asymptomatic girls with polyps however without malignant trans ormation risk actors, management can be more conservative. Some advocate elimination o all endometrial polyps as a outcome of premalignant and malignant trans ormation has been identi ed in even asymptomatic premenopausal girls (Golan, 2010). However, the trans ormation threat in these patients with small lesions is low, and many o these polyps spontaneously resolve or slough (Ben-Arie, 2004; DeWaay, 2002). I conservative observation is elected, the optimum surveillance or these girls stays unde ned. They usually seem as single, pink, easy elongated plenty extending rom the endocervical canal. These widespread growths are ound more requently in multiparas and rarely in prepubertal emales. Many endocervical polyps are identi ed by visual inspection during pelvic examination. Color flow characteristic identifies a single feeder vessel, which is characteristic of a polyp. Endocervical polyps are usually benign, and premalignant or malignant trans ormation develops in less than 1 p.c (Chin, 2008; Schnatz, 2009). However, cervical most cancers can current as polypoid lots and may mimic these benign lesions. Others in the di erential analysis embody condyloma acuminata, leiomyoma, decidua, granulation tissue, endometrial polyp, or broadenoma. Results confirmed no preinvasive illness or cancer in polyps o asymptomatic ladies with normal cervical cytology (Long, 2013; MacKenzie, 2009). For removal, i the stalk is slender, endocervical polyps are grasped by ring orceps. The polyp is twisted repeatedly in regards to the base o its stalk to strangulate its eeding vessels. Monsel paste (erric subsul ate) may be utilized with direct pressure to the resulting stalk stub to complete hemostasis. Rarely, a thick pedicle is ound and may warrant surgical ligation and excision i heavier bleeding is anticipated. Patients are counseled that polyp recurrence rates range rom 6 to 15 p.c (Berzolla, 2007; Younis, 2010). Symptoms can seem slowly or all of a sudden with li e-threatening bleeding (immerman, 2003). Sonographic characteristics are nonspeci c and should embrace anechoic tubular buildings throughout the myometrium. Color Doppler or energy Doppler ultrasound may present a more speci c picture with bright, large-caliber vessels and multidirectional ow (ullius, 2015). Angiography aids con rmation and can be utilized concurrently to per orm vessel embolization (Cura, 2009). In contrast, trauma or vaginal erosion rom a oreign physique is in requently encountered. O these, copper-containing intrauterine units (ParaGard) can cause heavy or intermenstrual bleeding, and a variety of other explanations have been instructed. At the cellular degree, prostaglandins are implicated as a ecting vascular tone (Coskun, 2011). At the tissue level, endometrial vascularity, congestion, and degeneration result in interstitial hemorrhage, which may result in intermenstrual bleeding (Shaw, 1979). They can also arise concurrently with cervical or endometrial cancer, with gestational trophoblastic illness, or with intrauterine device use (Ghosh, 1986). Intermenstrual bleeding, however, is typically not improved with these agents (God rey, 2013). Limited proof additionally helps tranexamic acid or treatment or prevention (Ylikorkala, 1983). Importantly, endometrial biopsy with small catheters can be per ormed without device elimination (Grimes, 2007). The endometrial e ects o progestins are thought to predominate, and evidence is accruing that low-dose progestins increase endometrial vascular ragility (Hickey, 2002). Over time, the endometrium atrophies, and these vascular abnormalities gradually resolve at a time thought to coincide clinically with progestin-induced amenorrhea (McGavigan, 2003).
Flutamide 250 mg order visa
Midline longitudinal sonogram of the pelvis in this 3-year-old woman demonstrates the uterus posterior to the bladder medicine technology 250 mg flutamide order free shipping. In most girls symptoms stomach cancer flutamide 250 mg buy otc, breast budding, termed thelarche, is the rst physical sign o puberty and begins at roughly age 10 years (Aksglaede, 2009; Biro, 2006). Following breast and pubic hair growth, adolescents undergo an accelerated enhance in peak, termed a development spurt, throughout a 3-year span rom ages 10. Prior to this age, particular person state laws govern whether minors can give their very own consent or sure kinds o well being care. Some examples embrace: emergency contraception, substance abuse, or sexually transmitted illness treatment. Congenital anomalies which may be seen externally, such as imper orate hymen, may be identi ed. Alternatively, i father or mother or child has a speci c complaint relating to vulvovaginal ache, rash, bleeding, discharge, or lesions, a gynecologic examination is directed towards the area o concern. Moreover, clinicians can use this chance to in orm a parent relating to ndings and potential remedy. They can even emphasize the idea o inappropriate genital touching by others and parental noti cation i this happens. In mid-to-late adolescence, nevertheless, a affected person may pre er, or privacy reasons, to not be examined with a mother or father present. Similarly, utilizing an anatomically acceptable doll to clarify the steps might decrease anxiety. The examination begins with a less-threatening approach o checking the ears, throat, heart, and lungs. The external genital examination is finest per ormed with the kid in a rog-leg or knee-chest place to improve visualization. Once the kid is optimally positioned, every labium could also be gently held with a thumb and ore nger and pulled towards the examiner and laterally. In this manner, the introitus, hymen, and decrease portion o the vagina are inspected. Vaginoscopy may be per ormed using a hysteroscope or cystoscope to provide illumination as well as irrigation. The labia majora are manually approximated to occlude the vagina and achieve vaginal distention. This usion might stay an isolated minor nding or may progress toward the clitoris to completely close the vaginal ori ce. Also termed labial agglutination, this adhesion develops in 1 to 5 percent o prepubertal ladies and in roughly 10 % o emale in ants within the rst 12 months o li e (Berenson, 1992; Christensen, 1971). Occasionally, with overuse o estrogen cream, native irritation, vulvar pigmentation, and minor breast budding may develop, at which time topical treatment is discontinued. Manual separation o labial adhesion in an outpatient setting without analgesia is ache ul and thus generally not suggested. However, i the adhesion persists regardless of constant use o estrogen cream, then labia minora separation could additionally be attempted a number of minutes a ter making use of 5-percent lidocaine ointment to the adhesion raphe. Typical for prepubertal ladies, the cervix is nearly flush with the proximal vagina. Additionally, erosion o the vulvar epithelium is implicated in some cases o labial adhesion. For example, adhesion could be associated with lichen sclerosus, with herpes simplex viral in ection, and with vulvar trauma ollowing sexual abuse (Berkowitz, 1987). The labia majora appear regular, whereas the labia minora are used with a definite skinny line o demarcation or raphe between them. Extensive agglutination may leave solely a ventral pinhole meatus between the labia. Located instantly beneath the clitoris, this small opening could lead to urinary dribbling as urine pools behind the adhesion. In many cases, i the patient is asymptomatic, no intervention is important as the adhesion will sometimes resolve spontaneously with the rise o estrogen levels at puberty. Extensive adhesion with urinary symptoms, nonetheless, would require estrogen cream remedy. Estradiol (Estrace) cream or conjugated equine estrogen (Premarin) cream is applied to the ne, thin raphe twice every day or 2 weeks, ollowed by every day purposes or an additional 2 weeks. A generous peasized quantity o cream is placed with a nger or cotton-tipped applicator onto the raphe. With every software, mild outward traction is exerted on the labia majora to assist separate the adhesion. Similarly, mild stress may also be applied with the cotton applicator itsel, as tolerated. A ter adhesion separation, a petroleum jelly (Vaseline) or nutritional vitamins A and D ointment (A&D ointment) may be applied nightly or 6 months to lower the danger o recurrence. These are o ten recognized in an adolescent with major amenorrhea and cyclic pain. Allergic and get in touch with dermatitis are common, whereas atopic dermatitis (eczema) and psoriasis are much less requent sources o itching and rash. With allergic and get in contact with dermatitis the underlying pathophysiology varies, however the medical appearance is often comparable. In response, in ormation regarding the degree o hygiene and continence and publicity to potential pores and skin irritants is sought. For most, eradicating the o ending agent and encouraging once- or twice-daily sitz baths is suf cient. These baths consist o putting two tablespoons o baking soda in warm water and soaking or 20 minutes. I itching is extreme, an oral medicine could additionally be prescribed, similar to hydroxyzine hydrochloride (Atarax) 2 mg/kg/d divided in our doses. Aside rom chemical irritants, kids can also develop diaper dermatitis rom urine and stool exposure. Corrective measures maintain the pores and skin dry by extra requent diaper modifications, or they create a moisture barrier by utility o emollient creams, such as Vaseline or A&D ointment. Findings include thin, parchment-like skin on the labia majora, ecchymoses on the labia minora and majora, and mild disease on the perianal pores and skin. Involvement of each the vulva and perinal pores and skin offers a figure-of-eight shape to affected areas. With this, the vulva shows hypopigmentation; atrophic, parchmentlike pores and skin; and occasional ssuring. Lesions are normally symmetrical and should orm an "hourglass" look around the vulva and perianal areas. Over time, i le t untreated, the periclitoral area might scar, the labia minora may become attenuated, and the posterior ourchette might ssure and bleed.

Generic 250 mg flutamide visa
The enamel is drawn to present the enamel rods extending from the dentinoenamel junction to the floor of the tooth medicine world flutamide 250 mg cheap overnight delivery. Although the full thickness of the enamel is fashioned treatment quietus tinnitus flutamide 250 mg sale, the full thickness of the dentin has not but been established. The contour strains within the dentin present the extent to which the dentin has developed at a particular time, as labeled in the illustration. Note that the pulp cavity within the center of the tooth turns into smaller because the dentin develops. This electron micrograph reveals a area of the Golgi equipment containing numerous giant vesicles. Note the abacus bodies (arrows) that include parallel arrays of filaments studded with granules. During their differentiation into odontoblasts, the cytoplasmic quantity and organelles characteristic of collagen-producing cells increase. The cells type a layer at the periphery of the dental papilla, and so they secrete the organic matrix of dentin, or predentin, at their apical end (away from the dental papilla;. A wave of mineralization follows the receding odontoblasts; this mineralized product is the dentin. As the cells transfer centrally, the odontoblastic processes elongate; the longest are surrounded by the mineralized dentin. In newly formed dentin, the wall of the dentinal tubule is solely the sting of the mineralized dentin. With time, the dentin immediately surrounding the dentinal tubule becomes extra highly mineralized; this more mineralized sheath of dentin is referred to as the peritubular dentin. Dental Pulp and Central Pulp Cavity (Pulp Chamber) the dental pulp cavity is a connective tissue compartment bounded by the tooth dentin. The cell incorporates a great amount of rough endoplasmic reticulum and a large Golgi equipment. The tissue has been handled with pyroantimonate, which forms a black precipitate with calcium. The blood vessels and nerves enter the pulp cavity on the tip (apex) of the foundation, at a site known as the apical foramen. This electron micrograph shows a means of the odontoblast coming into a dentinal tubule. The course of extends into the predentin and, after passing the mineralization front (arrows), lies within the dentin. The collagen fibrils within the predentin are finer than the extra mature, coarser fibrils of the mineralization front and past. Some bare nerve fibers additionally enter the proximal portions of the dentinal tubules and get in contact with odontoblast processes. The odontoblast processes are believed to serve a transducer perform in transmitting stimuli from the tooth surface to the nerves within the dental pulp. In teeth with multiple cusp, pulpal horns prolong into the cusps and contain giant numbers of nerve fibers. Because dentin continues to be secreted all through life, the pulp cavity decreases in quantity with age. This schematic diagram of gingiva corresponds to the oblong space of the orientation diagram. Elsewhere, the gingival epithelium is deeply indented by connective tissue papillae, and the junction between the 2 is irregular. The black strains represent collagen fibers from the cementum of the tooth and from the crest of the alveolar bone that extend toward the gingival epithelium. Note the shallow papillae within the lining mucosa (alveolar mucosa) that distinction sharply with these of the gingiva. Supporting Tissues of the Teeth Supporting tissues of the enamel embrace the alveolar bone of the alveolar processes of the maxilla and mandible, periodontal ligaments, and gingiva. The alveolar processes of the maxilla and mandible contain the sockets or alveoli for the roots of the enamel. The surface of the alveolar bone correct often reveals regions of bone resorption and bone deposition, particularly when a tooth is being moved. Periodontal illness normally results in lack of alveolar bone, as does the absence of useful occlusion of a tooth with its regular opposing tooth. The periodontal ligament is the fibrous connective tissue becoming a member of the tooth to its surrounding bone. This ligament � � � Bone reworking (during motion of a tooth) Proprioception Tooth eruption A histologic section of the periodontal ligament exhibits that it incorporates areas of both dense and loose connective tissue. The dense connective tissue incorporates collagen fibers and fibroblasts which may be elongated parallel to the long axis of the collagen fibers. The fibroblasts are believed to transfer backwards and forwards, forsaking a path of collagen fibers. Periodontal fibroblasts additionally comprise internalized collagen fibrils which are digested by the hydrolytic enzymes of the cytoplasmic lysosomes. These observations indicate that the fibroblasts not only produce collagen fibrils but also resorb collagen fibrils, thereby adjusting constantly to the demands of tooth stress and motion. The free connective tissue within the periodontal ligament accommodates blood vessels and nerve endings. In addition to fibroblasts and skinny collagenous fibers, the periodontal ligament also contains thin, longitudinally disposed oxytalan fibers. The submandibular gland is located underneath the ground of the mouth, within the submandibular triangle of the neck. The sublingual gland is positioned in the flooring of the mouth anterior to the submandibular gland. The minor salivary glands are located in the submucosa of various elements of the oral cavity. Initially, the gland takes the form of a solid cord of cells that enters the mesenchyme. The proliferation of epithelial cells ultimately produces extremely branched epithelial cords with bulbous ends. Degeneration of the innermost cells of the cords and bulbous ends results in their canalization. The gingiva is a specialised a part of the oral mucosa positioned around the neck of the tooth. The gingiva consists of two elements: � � the main salivary glands are surrounded by a capsule of reasonably dense connective tissue from which septa divide the secretory parts of the gland into lobes and lobules. The connective tissue related to the groups of secretory acini blends imperceptibly into the surrounding free connective tissue.
250 mg flutamide purchase free shipping
The kinds of connective tissue fibers are: � � � collagen fibers reticular fibers elastic fibers Collagen Fibers and Fibrils Collagen fibers are essentially the most ample type of connective tissue fiber medicine 3 sixes 250 mg flutamide with mastercard. In the sunshine microscope medicine grinder 250 mg flutamide discount overnight delivery, collagen fibers usually seem as wavy constructions of variable width and indeterminate size. Within a person fiber, the collagen fibrils are relatively uniform in diameter. In completely different areas and at different levels of development, nonetheless, the fibrils differ in dimension. In developing or immature tissues, the fibrils could additionally be as small as 15 or 20 nm in diameter. In dense regular connective tissue found in tendons or other tissues which are topic to appreciable stress, they could measure up to 300 nm in diameter. Electron micrograph of dense irregular connective tissue from the capsule of the testis of a young male. The thread-like collagen fibrils are aggregated in some areas (X) to type comparatively thick bundles; in different areas, the fibrils are more dispersed. A longitudinal array of collagen fibrils from the identical specimen seen at higher magnification. The collagen molecule (formerly called tropocollagen) measures about 300 nm long by 1. Within every fibril, the collagen molecules align head to tail in overlapping rows with a niche between the molecules in every row and a one-quarter-molecule stagger between adjacent rows. The tensile strength of the fibril is created by the covalent bonds between the collagen molecules of adjacent rows, not the head-to-tail attachment of the molecules in a row. Each collagen molecule is a triple helix composed of three intertwined polypeptide chains. Every third amino acid in the chain is a glycine molecule, except on the ends of the chains. A hydroxyproline or hydroxylysine incessantly precedes every glycine within the chain, and a proline incessantly follows each glycine within the chain. Along with proline and hydroxyproline, the glycine is essential for the triple-helix conformation. Associated with the helix are sugar teams that are joined to hydroxylysyl residues. A collagen fibril displays periodic banding with a distance (D) of sixty eight nm between repeating bands. Each fibril is self-assembled from staggered collagen molecules, that are covalently cross-linked with lysine and hydroxylysine residues in adjoining molecules (purple links). The collagen molecule is a triple helix cross-linked by quite a few hydrogen bonds between prolines and glycines. The X place following glycine is regularly a proline, and the Y position preceding the glycine is regularly a hydroxyproline. This atomic force microscopic picture of kind I collagen fibrils in the connective tissue shows the banding pattern on the floor of collagen fibrils. Note the random orientation of collagen fibrils that overlie and crisscross each other in the connective tissue matrix. To date, at least 42 types of chains encoded by completely different genes have been recognized and mapped to loci on a quantity of completely different chromosomes. As many as 29 various varieties of collagens have been categorized on the idea of the combinations of chains they include. A collagen molecule could additionally be homotrimeric (consisting of three identical chains) or heterotrimeric (consisting of two or even three genetically distinct chains). For instance, sort I collagen present in loose and dense connective tissue is heterotrimeric. Two of the chains, recognized as 1, are similar, and one, identified as 2, is totally different. The Roman numerals in the parentheses in the Composition column point out that the chains have a distinctive construction that differs from the chains with different numerals. Several lessons of collagens are identified on the premise of their polymerization sample. These varieties are characterised by uninterrupted glycine�proline�hydroxyproline repeats and aggregate to type 68-nm-banded fibrils (as diagramed in. Biosynthesis and Degradation of Collagen Fibers Collagen fiber formation entails events that occur both within and outside the fibroblast. Hydroxylation of proline and lysine residues (vitamin C required) and cleavage of signal sequence from pro� chain 5. Stabilization of the triple helix by formation of intra- and interchain hydrogen and disulfide bounds and chaperone proteins. Movement of vesicles to plasma membrane, assisted by molecular motor proteins associated with microtubules extracellular occasions 11. Cleavage of trimeric globular C- and helical N-procollagen domains by procollagen N- and C-proteinases 13. Polymerization (self-assembly) of collagen molecules into collagen fibrils (in cove of fibroblast) with improvement of covalent cross-linking 14. Schematic illustration of the biosynthetic events and organelles taking part in collagen synthesis. Bold numbers correspond to the occasions numbered in collagen biosynthesis listed on the backside. In basic, the synthetic pathway for collagen molecules is much like other constitutive secretory pathways used by the cell. The unique options of collagen biosynthesis are expressed in multiple posttranslational processing steps which are required to prepare the molecule for the extracellular assembly course of. Proline and lysine residues are hydroxylated while the polypeptides are still in the nonhelical conformation. This explains why wounds fail to heal and bone formation is impaired in scurvy (vitamin C deficiency). O-linked sugar groups are added to some hydroxylysine residues (glycosylation), and N-linked sugars are added to the 2 terminal positions. The globular structure is shaped at the carboxyterminus, which is stabilized by disulfide bonds. Formation of this structure ensures the correct alignment of the three chains during the formation of the triple helix. A triple helix (beginning from the carboxy-terminus) is formed by three chains, besides on the terminals where the polypeptide chains remain uncoiled. Intrachain and interchain hydrogen and disulfide bonds type that affect the form of the molecule. The triple-helix molecule is stabilized by the binding of the chaperone protein hsp47, which additionally prevents the untimely aggregation of the trimers within the cell. The folded procollagen molecules move to the Golgi equipment and begin to associate into small bundles. This bundling is achieved by the lateral associations between uncoiled terminals of the procollagen molecules.
Flutamide 250 mg order with visa
Cell-to-Extracellular Matrix Junctions the organization of cells in epithelium is determined by the help provided by the extracellular matrix on which the basal surface of each cell rests medications 2 flutamide 250 mg cheap on line. Anchoring junctions preserve the morphologic integrity of the epithelium�connective tissue interface sewage treatment buy flutamide 250 mg cheap. The two major anchoring junctions are: � � focal adhesions, which anchor actin filaments of the cytoskeleton into the basement membrane; and hemidesmosomes, which anchor the intermedi- ate filaments of the cytoskeleton into the basement membrane. Focal adhesions are also present in different nonepithelial cells similar to fibroblasts and easy muscle cells. In general, focal adhesions encompass a cytoplasmic face to which actin filaments are bound, a transmembrane connecting area, and an extracellular face that binds to the proteins of the extracellular matrix. The major family of transmembrane proteins involved in focal adhesions is integrins, that are concentrated in clusters inside the areas where the junctions could be detected. On the cytoplasmic face, integrins work together with actin-binding proteins (-actinin, vinculin, talin, paxillin) in addition to many regulatory proteins such as focal adhesion kinase or tyrosine kinase. On the extracellular aspect, integrins bind to extracellular matrix glycoproteins, usually laminin and fibronectin. Focal adhesions play an important role in sensing and transmitting indicators from the extracellular environment into the interior of the cell. Focal adhesions create a dynamic link between the actin cytoskeleton and extracellular matrix proteins. They are able to detect Focal adhesions kind a structural hyperlink between the actin cytoskeleton and extracellular matrix proteins. They are liable for attaching lengthy bundles of actin filaments (stress fibers) into the basal lamina. Focal adhesions play a prominent role during dynamic changes that happen in epithelial cells. Coordinated transforming of the actin cytoskeleton and the managed formation and dismantling of focal adhesions contractile forces or mechanical changes in the extracellular matrix and convert them into biochemical signals. This phenomenon, known as mechanosensitivity, permits cells to alter their adhesion-mediated functions in response to exterior mechanical stimuli. Integrins transmit these alerts to the interior of the cell, the place they affect cell migration, differentiation, and progress. Recent studies point out that focal adhesion proteins additionally serve as a typical level of entry for signals ensuing from stimulation of assorted courses of progress issue receptors. On the cytoplasmic aspect, observe the association of various actin-binding proteins. These proteins interact with integrins, the transmembrane proteins, the extracellular domains of which bind to proteins of the extracellular matrix. This picture was obtained from the fluorescence microscope and exhibits cells cultured on the fibronectin-coated floor stained with fluorescein-labeled phalloidin to visualize actin filaments (stress fibers) in green. Next, using indirect immunofluorescence methods, focal adhesions were labeled with major monoclonal antibody in opposition to phosphotyrosines and visualized with secondary rhodamine-labeled antibody (red). The phosphotyrosine is a product of the tyrosine kinase response by which tyrosine molecules of the related proteins are phosphorylated by this enzyme. Tyrosine kinase is carefully related to focal adhesion molecules, so the world the place focal adhesions are formed is labeled red. Note the relationship of focal adhesions and actin filaments at the periphery of the cell. A variant of the anchoring junction much like the desmosome is found in certain epithelia subject to abrasion and mechanical shearing forces that might are most likely to separate the epithelium from the underlying connective tissue. Typically, it happens in the cornea, the skin, and the mucosa of the oral cavity, esophagus, and vagina. In these places, it appears as if half the desmosome is current, therefore the name hemidesmosome. Hemidesmosomes are discovered on the basal cell floor, where they supply elevated adhesion to the basal lamina. The protein composition of this structure is much like that of the desmosomal plaque, as it contains a desmoplakin-like family of proteins able to anchoring intermediate filaments of the cytoskeleton. In contrast to the desmosome, whose transmembrane proteins belong to the cadherin household of calcium-dependent molecules, nearly all of transmembrane proteins found in the hemidesmosome belong to the integrin class of cell matrix receptors. These include: � � � Epithelial Tissue Plectin (450 kDa) capabilities as a cross-linker of the intermediate filaments that bind them to the hemidesmosomal attachment plaque. On the extracellular floor of the hemidesmosome, laminin molecules type threadlike anchoring filaments that stretch from the integrin molecules to the construction of the basement membrane. Interaction between laminin-332 and 6 four integrin stabilizes hemidesmosomes and is essential for hemidesmosome formation and for the maintenance of epithelial adhesion. Mutation of the genes encoding laminin-332 chains leads to junctional epidermolysis bullosa, one other hereditary blistering pores and skin illness. Below the nucleus (N), intermediate filaments are seen converging on the intracellular attachment plaques (arrows) of the hemidesmosome. Note that the intermediate filaments appear to originate or terminate within the intracellular attachment plaque. They attach the basal cell membrane of epithelial cells into the underlying basal lamina. Because of this phenomenon, the salivary gland ducts that possess these cells are referred to as striated ducts. They considerably increase the floor space of the basal cell area, permitting for more transport proteins and channels to be present. These basal surface modifications are outstanding in cells that participate in lively transport of molecules. In addition, mitochondria are sometimes concentrated at this basal web site to present the energy necessities for active transport. The orientation of the mitochondria, mixed with the basal membrane infoldings, results in a � � Exocrine glands secrete their products onto a surface immediately or through epithelial ducts or tubes which are related to a floor. Ducts might convey the secreted materials in an unaltered type or could modify the secretion by concentrating it or adding or reabsorbing constituent substances. They secrete their merchandise into the connective tissue, from which they enter the bloodstream to reach their goal cells. Cells that produce paracrine substances (paracrines) launch them into the subjacent extracellular matrix. The paracrine secretion has very limited signaling vary; it reaches the goal cells by diffusion. For instance, the endothelial cells of the blood vessels impact the vascular easy muscle cells by releasing multiple factors that cause both contraction or leisure of the vascular wall. In addition, many cells secrete molecules that bind to receptors on the same cell that launch them.
Real Experiences: Customer Reviews on Flutamide
Darmok, 22 years: The National Campaign to Prevent een Pregnancy, Washington, 2001 Kirby D: Reducing adolescent being pregnant: approaches that work. Troponin-T (TnT), a 30 kDa subunit, binds to tropomyosin, anchoring the troponin complicated. J Vasc Interv Radiol 25(5):725, 2014 Proctor M, Farquhar C: Diagnosis and administration o dysmenorrhoea. The erythrocytes appear in single file in one of many capillaries (the different two are empty).
Aila, 37 years: Swab specimens rom vagina, rather than endocervix, are really helpful or prepubertal girls (Centers or Disease Control and Prevention, 2015). However, in prescribing benzodiazepines, warning is taken in girls with prior history o substance abuse (Nevatte, 2013). Osteocytes are usually smaller than their precursor cells because of their decreased perinuclear cytoplasm. The vascular pericytes found round capillaries and venules are mesenchymal stem cells.
Uruk, 35 years: T us, girls with pelvic plenty and preoperative ndings suspicious or malignancy are typically re erred. Later, a similar epiphyseal ossification heart varieties on the distal end of the bone (see illustration eight of. Channels in gap junctions can fluctuate quickly between an open and a closed state through reversible modifications in the conformation of individual connexins. The lymphatic vessels originate in the white pulp near the trabeculae and represent a route for lymphocytes leaving the spleen.
8 of 10 - Review by M. Kor-Shach
Votes: 345 votes
Total customer reviews: 345